Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science Extra Questions

Chapter 3 Metals And Non-Metals Extra Questions and Answer
Chapter Name | Metal And Non - Metal Extra Questions |
Class | CBSE Class 10 |
Textbook Name | Metal And Non - Metal Class 10 |
Related Readings |
|
Question 1. Name the property due to which metals have a shining surface in their pure state.
Answer
Metallic lustre.
Question 2. Name two most malleable metals.
Answer
Gold and silver.
Question 3. Name the most ductile metal.
Answer
Gold.
Question 4. Name a metal which occurs in the free state.
Answer
Gold.
Question 5. Give an example of an elementary substance which is a good conductor of electricity but is not a metal.
Answer
Graphite.
Question 6. Name two metals which are both malleable and ductile.
Answer
Silver and gold.
Question 7. Name the non-metal which is a liquid.
Answer
Bromine.
Question 8. Expand PVC.
Answer
Polyvinyl chloride.
Question 9. Name a non-metal which is lustrous.
Answer
Iodine.
Question 10. Metal A can displace metal B from BO, the oxide of metal B. Metal B can displace C from solution of CSO4, the sulphate of metal C. Arrange metal A, B and C in the order of increasing reactivity.
Answer
C < B < A.
Question 11. Name two metals which can be cut with a knife.
Answer
Lithium, sodium, potassium
Question 12. An element forms an oxide A2O3 which is acidic in nature. Identify A as a metal or non-metal. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
Oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature while those of metals are basic in nature. Hence, A must be a non-metal.
Question 13. Why does calcium float in water?
Answer
Calcium reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen. Bubbles of hydrogen gas stick to the surface of calcium, hence it floats.
Question 14. Arrange the following metals in the decreasing order of reactivity Na, K, Cu, Ag.
Answer
K > Na > Cu > Ag.
Question 15. Name the two metals which do not react with water at all.
Answer
Lead, Copper, Silver and Gold
Question 16. Name the element which shows non-metallic properties, but is also present in the activity series of metal.
Answer
Hydrogen.
Question 17. If X, Y, Z, W, A, B and C represents the metals in the decreasing order of their reactivity, which metal is most likely to occur in free state in nature?
Answer
C is least reactive, hence .it is likely to occur in the free state.
Question 18. Name any one metal which reacts neither with cold water nor with hot water, but reacts with heated steam to produce hydrogen gas.
Answer
Iron
3Fe (s) + 4H2O (g) → Fe3O4 (s) + 4H2 (g)
Question 19. Mention the composition of aqua regia.
Answer
It is a freshly prepared mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid in the ratio of 3:1.
Question 20. In nature, metal A is found in the free state, while metal B is found in the form of its compounds. Which of these two will be nearer to the top of the activity series of metals?
Answer
Metal B will be nearer to the top because it is more reactive as it is clear from the fact that it exists in the form of its compounds.
Question 21. Name any two oxides ores.
Answer
- Haematite
- Bauxite.
Question 22. Which method is used for the concentration of sulphide ores?
Answer
Froth flotation process.
Question 23. Complete the chemical equation.
Answer
Question 24. What is galvanisation?
Answer
Galvanisation is a method of protecting steel and iron from rusting by coating them with a thin layer of zinc.
Question 25. 24 Carat gold is not suitable for making jewellery. Why?
Answer
24 carat gold is very soft, so it is alloyed with either silver or copper to make it hard.
Question 26. How many carats is pure gold?
Answer
24 carat.
Question 27. Name the metal which is used for galvanising iron.
Answer
Zinc (Zn).
Question 28. What is meant by 22 carat gold?
Answer
An alloy consisting of 22 parts by weight of pure gold and 2 parts by weight of copper or silver is called 22 carat gold.
Question 29. What is an alloy?
Answer
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal.
Question 30. Why do shopkeepers apply oil on tools made of iron while storing them?
Answer
To protect them from rusting as the oxygen and moisture of the atmosphere will not be able to come in direct contact with the surface of iron.
Question 31. State two conditions for the rusting of iron.
Answer
- Presence of air (or oxygen).
- Presence of water (or moisture).
Question 32. Name two metals which are highly resistant to corrosion.
Answer
Gold and platinum.
Question 33. Name the gas in air which tarnishes silver particles slowly.
Answer
Hydrogen sulphide (H2S).
Short Answer Type I Questions
Question 1. What happens when
(a) ZnCO3 is heated in the absence of oxygen?
(b) a mixture of Cu2O and Cu2S is heated? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
(a) A mixture of ZnO(s) and CO2 is formed.
(b) A mixture of copper and SO2 is formed![]()
Question 2. Using the electronic configurations, explain how magnesium atom combines with oxygen atom to form magnesium oxide by transfer of electrons.
Answer

Question 3. Name two metals which react violently with cold water. Write any three observations you would make when such a metal is dropped into water. How would you identify the gas evolved, if any, during the reaction? [CBSE 2008]
Answer
Sodium, Potassium
When these metals are dropped in water, bubbles will be evolved due to evolution of hydrogen gas.
The gas will catch fire and the solution will be alkaline, i.e., it will turn red litmus blue.
Test: When a burning matchstick is brought near the gas, it burns explosively with a ‘pop’ sound and the splinter is extinguished.
Question 4. State reasons for the following:
(i) Electric wires are covered with rubber-like material.
(ii) From dilute hydrochloric acid, zinc can liberate hydrogen gas but copper cannot.
Answer
(i) It is because rubber is an insulator and does not allow current to flow through it.
(ii) Zinc is is placed above hydrogen in the reactivity series of metals while copper is placed below it. Metals placed above hydrogen can displace hydrogen from water and acids while those below it cannot. Therefore, zinc can displace hydrogen from dilute HCl whereas copper cannot.
Question 5. Give the formulae of the stable binary compounds that would be formed by the combination of the following pairs of elements.
(a) Mg and N2
(b) Li and O2
(c) Al and Cl2
(d) K and O2
Answer
(a) Mg3N2
(b) Li2O
(c) AlCl3
(d) K2O
Question 6. Compound X and aluminium are used to join railway tracks.
(a) Identify the compound X
(b) Name the reaction
(c) Write down its reaction. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
(a) Compound X must be iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3.
(b) The reaction is known as ‘thermite reaction’ or ‘aluminothermy’.
(c) The reaction is carried out by igniting the mixture with a Mg-ribbon.![]()
Question 7. Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Answer
Zinc and magnesium can displace hydrogen from dilute acids whereas copper and silver cannot. The metals lying above hydrogen in the reactivity series can displace hydrogen on reaction with dilute acids.
Question 8. During extraction of metals, electrolytic refining is used to obtain pure metals,
(a) Which material will be used as anode and cathode for refining of silver metal by this process?
(b) Suggest a suitable electrolyte also,
(c) In this electrolytic cell, where do we get pure silver after passing electric current? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
In the electrolytic refining of impure silver metal:
(a) A rod of impure silver is used as anode while that of pure silver as cathode.
(b) The electrolyte is a water soluble salt of silver, for example silver chloride or silver nitrate.
(c) On passing current, pure silver gets deposited at the cathode. It can be scrapped off later on.
Question 9. Give reason for the following:
(i) Iron grills are frequently painted.
(ii) Gold ornaments retain their lustre even after several years of use.
Answer
(i) Iron metal easily gets rusted by air containing moisture and oxygen. Therefore, iron grills are frequently painted with rust proof paints.
(ii) Gold is a noble metal and is not affected by chemicals or by air. Therefore, gold ornaments retain their lustre even after several years.
Question 10. Name two metals which can be used to reduce metal oxides to metal.
Answer
(i) Aluminium (Al)
(ii) Magnesium (Mg)
Question 11. Give the reaction involved during extraction of zinc from its ore by
(a) roasting of zinc ore
(b) calcination of zinc ore [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
(a) Roasting is done for the sulphide ore (zinc blende).![]()
(b) Calcination is done for the carbonate ore (calamine).![]()
Question 12. The following reaction takes place when aluminium powder is heated with Manganese dioxide.
3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s) → 3Mn(l) + 2Al2O3(l) + Heat [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Is aluminium getting reduced?
(b) Is MnO2 getting oxidised?
Answer
(a) Aluminium is getting oxidised to Al2O3.
(b) Manganese dioxide is getting reduced to Mn.
Question 13. Differentiate between roasting and calcination process used in metallurgy. Give one example of each.
Answer

Question 14. Write chemical equations for the reactions taking place when
(a) Magnesium ribbon is burnt in a jar containing oxygen
(b) Sodium metal falls into a sink containing water
Answer
(a)
(b) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
Question 15. What is an amalgam? Write the constituent metals of brass.
Answer
An amalgam is an alloy in which one of the metals is mercury.
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc (Cu and Zn). It contains 80% copper and 20% zinc.
Question 16. Every ore is a mineral but not every mineral is an ore. Explain.
Answer
Every mineral is not suitable for the extraction of the metal. The mineral from which the metal is economically and conveniently extracted is called an ore.
Short Answer Type II Questions
Question 1. What is an alloy? How is it prepared? Name the alloy which is used for welding electrical wires together.
Answer
Alloy is a mixture of two or more metals or non-metals.
Alloys are made by mixing the metals in their molten state. It is prepared by first melting the primary metal and then dissolving the other metal in definite proportion. It is then cooled to room temperature. Solder is used for welding electrical wires together.
Question 2. Give reasons for the following observations:
(i) Ionic compounds in general have high melting and boiling points.
(ii) Highly reactive metals cannot be obtained from their oxides by heating them with carbon.
(iii) Copper vessels get a green coat when left exposed to air in the rainy season.
Answer
(i) Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to strong force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
(ii) It is because these metals, have great affinity towards oxygen and so cannot be reduced by carbon or carbon monoxide or hydrogen.
(iii) Copper vessels react with CO2, O2 and moisture to form green coloured basic copper carbonate [CuCO3. Cu(OH)2] on their surface when exposed to moist air.
Question 3. E is an element amongst copper, zinc, aluminium and iron. It shows the following properties:
(a) One of its ores is rich in E2O3.
(b) E2O3 is not attacked by water.
(c) It forms two chlorides ECl2 and ECl3.
Name the element and justify your answer.
Answer
The clue for the correct answer is the formation of ECl2 and ECl3. This shows that the element E has variable valencies of 2 and 3 out of the elements listed, only iron exists in divalent and trivalent forms.
(a) The ore rich in Fe2O3 is haematite.
(b) Haematite (Fe2O3) is not attacked by water.
(c) The two chlorides are: Iron (II) chloride or FeCl2 and iron (III) chloride or FeCl3.
Question 4. When a metal X is treated with cold water, it gives a basic salt Y with molecular formula XOH (Molecular mass = 40) and liberates a gas Z which easily catches fire. Identify X, Y and Z and also write the reaction involved. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
The base with molecular mass 40 is NaOH. Hence, the metal X must be sodium (Na). It reacts with H2O to form the base NaOH and liberates H2 gas which easily catches fire.
Question 5. You are provided with three metals: Sodium, magnesium and copper. Using only water as the reactant, how will you identify them?
Answer
- The metal which reacts violently with cold water and catches fire is sodium.
- The metal which evolves hydrogen gas upon heating with water is magnesium.
- The metal which does not react with water even on strong heating is copper.
Question 6. A non-metal A is an important constituent of our food and forms two oxides B and C. Oxide B is toxic whereas C causes global warming.
(a) Identify A, B and C.
(b) To which Group of Periodic Table does A belong? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
The non-metal A is carbon. It is an important constituent of our food in different forms. For example, glucose (C6H12O6) contains carbon. In fact, all food materials are organic compounds and these contain carbon as an essential constituent. The two oxides of carbon are, carbon monoxide (B) and carbon dioxide (C). Carbon dioxide causes global warming.
(a) A = Carbon (C); B = Carbon monoxide (CO); C = Carbon dioxide (CO2)
(b) Carbon is the first member of group 14 in the long form of periodic table.
Question 7. A non-metal X exists in two different forms Y and Z. Y is the hardest natural substance, whereas Z is a good conductor of electricity. Identify X, Y and Z. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
Non-metal ‘X’ must be carbon. It exist in two forms, diamond and graphite. Diamond is hardest natural substance. Hence, ‘Y’ is diamond. Graphite is a good conductor of electricity. Hence, ‘Z’ is graphite.
Question 8. A metal E is stored under kerosene. When a small piece of it is left open in air, it catches fire. When the product formed is dissolved in water, it turns red litmus to blue.
(i) Name the metal E.
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction when it is exposed to air and when the product is dissolved in water.
(iii) Explain the process by which the metal E is obtained from its molten chloride.
Answer
(i) The available information suggests that the metal (E) is sodium (Na).

The solution is basic and it turns red litmus blue.
(iii) The metal is obtained by the process of electrolytic reduction.
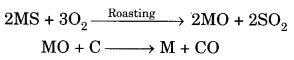
Question 9. Explain how the following metals are obtained from their compounds by reduction process:
(i) Metal X which is low in reactivity series
(ii) Metal Y which is in the middle of the series
(iii) Metal Z which is high up in the reactivity series.
Give one example of each type.
Answer
(i) Metals which are low in reactivity series can be obtained by heating their compounds. For example, mercury is obtained by heating its ore, cinnabar (HgS), in air.
HgS + O2 → Hg + SO2
(ii) Metals which are in the middle of the series are generally obtained by heating their compounds with some reducing agent such as carbon. For example, iron is obtained from haematite (Fe2O3) by reducti
Question 10. How is the method of extraction of metals high up in the reactivity series different from that for metal in the middle? Why the same process cannot be applied for them? Explain giving equations, the extraction of sodium.
Answer
The metals placed high up in the reactivity series (e.g., Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al) are highly reactive and strong reducing agents and are extracted by carrying out the electro-reduction of their molten salts. On the other hand, metals placed in the middle of the series (e.g., Fe, Zn, Cd, Co, Ni, etc.) are comparatively less reactive and are extracted by roasting or calcination.
Sodium is extracted by electro-reduction process.
NaCl ⇌ Na+ + Cl–
Reaction at the cathode: Na+ + e+ → Na+
Reaction at the anode: Cl– – e– → Cl
Cl + Cl → Cl2
Question 11. Write balanced chemical equation for the reactions taking place when
(i) zinc carbonate is calcinated.
(ii) zinc sulphide is roasted or heated in air.
(iii) zinc oxide is reduced to zinc.
Answer

Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Explain the following:
(a) Reactivity of Al decreases if it is dipped in HNO3.
(b) Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of Na or Mg.
(c) NaCl is not a conductor of electricity in solid state whereas it does conduct electricity in aqueous solution as well as in molten state.
(d) Iron articles are galvanised.
(e) Metals like Na, K, Ca and Mg are never found in their free state in nature. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
(a) On dipping in HNO2, the surface of Al is oxidised to form an oxide layer of Al2O3, which is hard and impervious. It acts as a protective layer for Al underneath. Hence, reactivity of Al decreases.
(b) Na or Mg are highly reactive metals. They have greater affinity for oxygen than for carbon. Hence, their oxides are stable. To reduce them with carbon, very high temperature is required. At this temperature, these metals react with carbon to form corresponding carbides.
(c) The conduction of electricity is due to movement of ions. In the solid state, Na+ and Cl– are fixed and not free to move. Hence, it does not conduct electricity. In the aqueous solution or in the molten state, Na+ and Cl– ions are free to move about and hence conduct electricity.
(d) Galvanisation means coating of iron articles with a layer of zinc. Zinc is more reactive than iron. Hence, it undergoes oxidation more readily than iron. As a result, iron articles remain protected.
(e) These metals are highly reactive and react with the gases present in the air. Hence, they are found as compounds in the ores and not in the free state in nature.
Question 2. (i) Given below are the steps for extraction of copper from its ore. Write the reaction involved.
(a) Roasting of copper (I) sulphide.
(b) Reduction of copper (I) oxide with copper (I) sulphide.
(c) Electrolytic refining.
(ii) Draw a neat and well labelled diagram for electrolytic refining of copper. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
(i)
This reaction in which one of the reactants (Cu2S) carries the reduction of the product (Cu2O) is known as auto-reduction.
(c) Reaction taking place in electrolytic refining are:
At cathode (reduction): Cu2 +(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
At anode (oxidation): Cu(s) → Cu2 + (aq) + 2e–
(ii) Metals like copper, aluminium and zinc are refined by this process.
Question 3. (a) In the formation of compound between two atoms A and B, A loses two electrons and B gains one electron.
(i) What is the nature of the bond between A and B?
(ii) Suggest the formula of the compound formed between A and B.
(b) On similar lines explain the formation of MgCl2 molecule.
(c) Common salt conducts electricity only in the molten state. Why?
(d) Why is melting point of NaCl high?
Answer
(a) (i) Ionic bond
(b) Mg → Mg2+ + 2e–
2Cl + 2e– → 2Cl–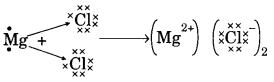
(c) Na+ and Cl– ions are free to move in molten state but not in solid state.
(d) It is due to strong force of attraction between Na+ and Cl–.
Question 4. Two ores A and B were taken. On heating ore A gives CO2 whereas, ore B gives SO2. What steps will you take to convert them into metals? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
Since ore A gives CO2 and ore B gives SO2. Therefore, ores are MCO3 and MS.
A can be obtained
B can be obtained
Metals and Non-metals HOTS Questions With Answers
Question 1. An element A burns with a golden yellow flame in air. It reacts with another element B,
atomic number 17 to give a product C. An aqueous solution of product C on electrolysis gives a compound D and liberates hydrogen. Identify A, B, C and D. Also write down the equations for the reactions involved. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
A = Sodium which burns with golden flame in air. It reacts with chlorine (Z = 17) to form sodium chloride.
2Na (s) + Cl2 (g) → 2NaCl (s)
Hence, B = chlorine and C = sodium chloride
Hence, D = Sodium hydroxide.
Question 2. What is meant by reactivity series of metals? State which of the following chemical reactions will take place giving suitable reason for each.
I. Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
II. Fe (s) + ZnSO4 (ag) → FeSO4 (aq) + Zn (s)
III. Zn (s) + FeSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Fe (s)
Answer
Reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in the order of their decreasing reactivity (activities).
I. Reaction will take place because Zn is above Cu in the activity series and is more reactive than Cu.
II. Reaction will not take place as Fe is below Zn in the activity series and cannot displace Zn from its solution.
III. Reaction will take place because Zn is more reactive than Fe.
Question 3. A student has been collecting silver coins and copper coins. One day, she observed a black coating on silver coins and a green coating on copper coins. Which chemical phenomenon is responsible for these coatings? Write the chemical name of black and green coatings.
Answer
The name of the phenomenon is corrosion. The chemical name of black coating is silver sulphide (Ag2S) formed due to attack of H2S gas present in the atmosphere on silver and that of green coating is basic copper carbonate formed due to attack of moist air (CO2, O2 and H2O vapours) on copper.
Question 4. Iqbal treated a lustrous, divalent element M with sodium hydroxide. He observed the formation of bubbles in the reaction mixture. He made the same observations when this element was treated with hydrochloric acid. Suggest how can he identify the produced gas. Write chemical equations for both the reactions. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
The divalent element M is a metal. It reacts with both sodium hydroxide (alkali) and dilute hydrochloric acid to evolve hydrogen gas.
M(s) + 2NaOH (aq) → Na2MO2 (aq) + H2(g)
M(s) + 2HCl (aq) → MCl2 (aq) + H2(g)
The gas burns with a pop sound when a burning matchstick is brought near it.
Question 5. A non-metal A which is the largest constituent of air, when heated with H2 in 1: 3 ratio in the presence of catalyst (Fe) gives a gas B. On heating with O2 it gives an oxide C. If this oxide is passed into water in the presence of air it gives an acid D which acts as a strong oxidising agent.
(a) Identify A, B, C and D.
(b) To which group of periodic table does this non-metal belong? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer
Non-metal which is the largest constituent of air is nitrogen (N2). Hence, A = N2.
When heated with H2 in presence of Fe as catalyst, it forms ammonia (NH3).
Hence, B = NH3.
When heated with O2, it forms nitric oxide (NO).
![]()
NO further gets oxidised to NO2 by O2 of the air.
2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
Hence, C = NO2.
On passing this oxide into water in presence of air (O2), it gives nitric acid (HNO3) which is a strong oxidising agent.
4NO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2(g) → 4HNO3(aq)
Hence, D = HNO3.
Nitrogen belongs to Group 15.
Value Based Questions
Question 1. Anil and his neighbour Sunil had got their garden fenced with iron rods. Next day Anil saw that Sunil was painting the iron fence. Sunil suggested Anil to do the same to increase the longevity of the iron rods by preventing corrosion. Anil argued that it is a waste of time and his iron rods were strong enough. After reading the above passage, answer the following questions.
(i) Whose opinion was correct? Justify.
(ii) Mention two methods (other than painting) to prevent iron from corrosion.
(iii) What is the chemical formula of rust?
(iv) Mention the values exhibited by Sunil.
Answer
(i) Sunil’s opinion is correct, it helps to protect iron rods from rusting/corrosion.
(ii) (a) Galvanisation
(b) Cathodic protection
(iii) Fe2O3. xH2O
(iv) Friendship/use of knowledge of Chemistry
Question 2. Mohan approached a goldsmith and asked him to make some gold ornaments. For this he gave advance money also and demanded that 100% pure gold ornaments be made. The goldsmith suggested Mohan that 22-carat gold ornaments would be more appropriate than 24-carat.
(i) What is the difference between 24-carat gold and 22-carat gold?
(ii) Calculate the % of gold in 22-carat gold.
(iii) Why did the goldsmith suggested for use of 22-carat gold?
(iv) Mention the values exhibited by the goldsmith.
Answer
(i) 24-carat gold is pure gold (100% pure gold) while 22-carat gold is comparatively less pure.
(ii) % of gold in 22 carat = 100 = 91.7%
(iii) Pure of 24-carat gold is very soft, little malleable and ductile. It is quite difficult to work on it. But 22 carat gold (alloy) is comparatively hard, more malleable and ductile.
(iv) Use of knowledge of chemistry, truth, honesty and professionalism.
