RS Aggarwal Solutions Chapter 16 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 16D Class 10 Maths

Chapter Name | RS Aggarwal Chapter 16 Coordinate Geometry |
Book Name | RS Aggarwal Mathematics for Class 10 |
Other Exercises |
|
Related Study | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths |
Exercise 16D Solutions
1. Points A(-1, y) and B(5, 7) lie on the circle with centre O(2, -3y). Find the value of y.
Solution
The given points are A(-1, y), B(5, 7) and O (2, -3y).
Here, AO and BO are the radii of the circle. So,
AO = BO ⇒ AO2 = BO2
⇒ (2 + 1)2 + (-3y – y)2 = (2 – 5)2 + (-3y – 7)2
⇒ 9 + (4y)2 = (-3)2 + (3y + 7)2
⇒ 9 + 16y2 = 9 + 9y2 + 49 + 42y
⇒ 7y2 – 42y – 49 = 0
⇒ y2 – 6y – 7 = 0
⇒ y2 – 7y + y – 7 = 0
⇒ y(y – 7) + 1(y – 7) = 0
⇒ (y – 7)(y + 1) = 0
⇒ y = -1 or y = 7
Hence, y = 7 or y = -1.
2. If the point A(0, 2) is equidistant from the points B(3, p) and C(p, 5), find p.
Solution
The given points are A(0, 2), B(3, p) and C(p, 5).
AB = AC ⇒ AB2 = AC2
⇒ (3 – 0)2 + (p – 2)2 = (p – 0)2 + (5 – 2)2
⇒ 9 + p2 – 4p + 4 = p2 + 9
⇒ 4p = 4
⇒ p = 1
Hence, p = 1
3. ABCD is a rectangle whose there vertices are A(4, 0), C(4, 3) and D(0, 3). Find the length of one of its diagonal.
Solution
The given vertices are B(4, 0), C(4, 3) and D(0, 3)
Here, BD one of the diagonals. So,
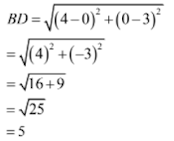
Hence, the length of the diagonal is 5 units.
4. If the point P(k – 1, 2) is equidistant from the points A(3, k) and B(k, 5), find the value of k.
Solution
The given points are P(k – 1, 2), A(3, k) and B(k, 5).
∵ AP = BP
∴ AP2 = BP2
⇒ (k – 1 – 3)2 + (2 – k)2 = (k – 1 – k)2 + (2 – 5)2
⇒ (k – 4)2 + (2 – k)2 = (-1)2 + (-3)2
⇒ k2 – 8y + 16 + 4 + k2 = 1 + 9
⇒ k2 – 6y + 5 = 0
⇒(k – 1)(k – 5) = 0
Hence, k = 1 or k = 5
5. Find the ratio in which the point P(x, 2) divides the join of A(12, 5) and B(4, -3).
Solution
Let k be the ratio in which the point P(x, 2) divides the line joining the points
A(x1 = 12, y1 = 5) and B(x2 = 4, y2 = -3). Then
x = (k × 4 + 12)/(k + 1) and 2 = (k × (-3) + 5)/(k + 1)
Now,
2 = {k × (-3) + 5}/(k + 1)
⇒ 2k + 2 = - 3k + 5
⇒ k = 3/5
Hence, the required ratio is 3 : 5.
6. Prove that the diagonals of a rectangle ABCD with vertices A(2, -1), B(5, -1), C(5, 6) and D(2, 6) are equal and bisect each other.
Solution
The vertices of the rectangle ABCD are A(2, -1), B(5, -1), C(5, 6) and D(2, 6). Now
Coordinates of midpoint of AC = (2 + 5)/2, (-1 + 6)/2 = (7/2, 5/2)
Coordinates of midpoint of BD = (5 + 2)/2, (-1 + 6)/2 = (7/2, 5/2)
Since, the midpoints of AC and BD coincide, therefore the diagonals of rectangle ABCD bisect each other.
7. Find the lengths of the median AD and BE of △ABC whose vertices are A(7, -3), B(5, 3) and C(3, -1).
Solution
The given vertices are A(7, -3), B(5, 3) and C( 3, -1).
Since D and E are the midpoints of BC and AC respectively. Therefore,
Coordinates of D = (5 + 3)/2, (3 - 1)/2 = (4, 1)
Coordinates of E = (7 + 3)/2, (-3 – 1)/2 = (5, -2)
Now,

Hence, AD = BE = 5 units.
8. If the point C(k, 4) divides the join of A(2, 6) and B(5, 1) in the ratio 2 : 3 then find the value of k.
Solution
Here, the point C(k, 4) divides the join of A(2, 6) and B(5, 1) in ratio 2 : 3. So
k = (2 × 5 + 3 × 2)/(2 + 3)
= (10 + 6)/5
= 16/5
Hence, k = 16/5
9. Find the point on x-axis which is equidistant from the points A(-1, 0) and B(5, 0)
Solution
Let P(x, 0) be the point on x-axis. Then
AP = BP ⇒ AP2 = BP2
⇒ (x + 1)2 + (0 – 0)2 = (x - 5)2 + (0 – 0)2
⇒ x2 + 2x + 1 = x2 – 10x + 25
⇒ 12x = 24
⇒ x = 2
Hence, x = 2
10. Find the distance between the points A(-8/5, 2) and B(2/5, 2)
Solution
The given points are A(-8/5, 2) and B(2/5, 2)
Then, (x1 = -8/5, y1 = 2) and (x2 = 2/5, y2 = 2)

Solution
The points (3, a) lies on the line 2x – 3y = 5.
If point (3, a) lies on the line 2x – 3y = 5, then 2x – 3y = 5
⇒ (2 × 3) – (3 × a) = 5
⇒ 6 – 3a = 5
⇒ 3a = 1
⇒ a = 1/3
Hence, the value of a is 1/3.
12. If the points A(4, 3) and B(x, 5) lie on the circle with center O(2, 3), find the value of x.
Solution
The given points A(4, 3) and B(x, 5) lie on the circle with center O(2, 3).
Then, OA = OB

⇒ (x – 2)2 = (22 – 22)
⇒ (x – 2)2 = 0
⇒ x – 2 = 0
⇒ x = 2
Hence, the value of x = 2.
13. If P(x, y) is equidistant from the point A(7, 1) and B(3, 5), find the relation between x and y.
Solution
Let the point P(x, y) be equidistant from the points A(7, 1) and B(3, 5)
Then,
PA = PB
⇒ PA2 = PB2
⇒ (x – 7)2 + (y – 1)2 = (x – 3)2 + (y – 5)2
⇒ x2 + y2 – 14x – 2y + 50 = x2 + y2 – 6x – 10y + 34
⇒ 8x – 8y = 16
⇒ x – y = 2
14. If the centroid △ABC having vertices A(a, b), B(b, c) and C(c, a) is the origin, then find the value of (a + b + c).
Solution
The given points are A(a, b), B(b, c) and C(c, a)
Here,
(x1 = a, y1 = b), (x2 = b, y2 = c) and (x3 = c, y3 = a)
Let the centroid be (x, y)
Then,
x = 1/3(x1 + x2 + x3)
= 1/3(a + b + c)
= (a + b + c)/3
y = 1/3(y1 + y2 + y3)
= 1/3(b + c + a)
= (a + b + c)/3
But it is given that the centroid of the triangle is the origin.
Then, we have:
(a + b + c)/3 = 0
⇒ a + b + c = 0
15. Find the centroid of △ABC whose vertices are A(2, 2), B(-4, -4) and C(5, -8).
Solution
The given points area A(2, 2), B(-4, -4) and C(5, -8)
Here, (x1 = 2, y1 = 2), (x2 = -4, y2 = -4) and (x3 = 5, y3 = -8)
Let G(x, y) be the centroid of △ABC. Then,
x = 1/3(x1 + x2 + x3)
= 1/3(2 – 4 + 5)
= 1
y = 1/3(y1 + y2 + y3)
= 1/3(2 – 4 – 8)
= -10/3
Hence, the centroid △ABC is G (1, -10/3).
16. In what ratio does the point C(4, 5) divides the join of A(2, 3) and B(7, 8) ?
Solution
Let the required ratio be k : l
Then, by section formula, the coordinates of C are
C(7k + 2)/(k + 1), (8k + 3)/(k + 1)
Therefore,
(7k + 2)/(k + 1) = 4 and (8k + 3)/(k + 1) = 5 [∵ C(4, 5) is given]
⇒ 7k + 2 = 4k + 4 and 8k + 3 = 5k + 5
⇒ 3k = 2
⇒ k = 2/3 in each case
So, the required ratio is 2/3 : 1, which is same as 2 : 3.
17. If the points A(2, 3), B(4, k) and C(6, -3) are collinear, find the value of k.
Solution
The given points are A(2, 3), B(4, k) and C(6, -3)
Here, (x1 = 2, y1 = 3), (x2 = 4, y2 = k) and (x3 = 6, y3 = -3)
It is given that the points A, B and C are collinear, Then,
x1(y2 – y3) + x2(y3 – y1) + x3(y1 – y2) = 0
⇒ 2(k + 3) + 4(- 3 – 3) + 6(3 – k) = 0
⇒ 2k + 6 – 24 + 18 – 6k = 0
⇒ - 4k = 0
⇒ k = 0
