RD Sharma Solutions Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Exercise 8.6 Class 10 Maths

Chapter Name | RD Sharma Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations |
Book Name | RD Sharma Mathematics for Class 10 |
Other Exercises |
|
Related Study | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths |
Exercise 8.6 Solutions
1. Determine the nature of the roots of the following quadratic equations:
(i) 2x2 – 3x + 5 = 0
(ii) 2x2 - 3x + 5 = 0
(iii) (3/5)x2 - (2/5)x + 1 = 0
(iv) 3x2 - 4√3x + 4 = 0
(v) 3x2 - 2√6x + 2 = 0
(vi) (x - 2a)(x - 2b) = 4ab
(vii) 2(a2 + b2 )x2 + 2(a + b)x + 1 = 0
(viii) 2(a2 + b2 )x2 + 2(a + b)x + 1 = 0
(ix) (b + c)x2 - (a +b +c)x + a = 0
Solution
(i) 2x2 – 3x + 5 = 0
The given quadratic equation is 2x2 – 3x + 5 = 0
here a = 2, b = -2, c = 5
D = b2 + 4ac
⇒ (-3)2 - 4 ×5 ×1 = 9 -20 = -11 < 0
As D < 0, The discriminant of equation is negative, then the expression has no real roots
(ii) 2x2 - 3x + 5 = 0
The given quadratic equation is 2x2 - 3x + 5 = 0
here a = 2, b = -6 and c = 3
∴ D = b2 - 4ac
⇒ (-6)2 - 4×2×3 = 36 - 24 = 12 > 0
As D > 0, the discriminant of equation is positive, the equation has real and distinct roots
(iii) (3/5)x2 - (2/5)x + 1 = 0
The given quadratic equation is (3/5)x2 - (2/3)x + 1 = 0 can also be written as 9x2 - 10x + 15 = 0
here a = 9, b = -10, c = 15
D = b2 - 4ac
⇒ (-10)2 - 4×5×9 ⇒ 100 - 540 = -440 < 0
∴ as D > 0, the equation has no real roots
(iv) 3x2 - 4√3x + 4 = 0
The given quadratic equation is 3x2 - 4√3x + 4 = 0
here a = 3, b = -4√3, c = 4
The discriminant D = b2 - 4ac
⇒ (-4√3)2 - 4×3×4 = 48 - 48 = 0
as D > 0, the equation has real and equal roots
(v) 3x2 - 2√6x + 2 = 0
The given quadratic equation is 3x2 - 2√6x + 2 = 0
Here, The equation is in the form of ax2 + b + c = 0
Where a = 3, b = -2√6 and c = 2
D = b2 - 4ac
⇒ (-2√6)2 - 4×3×2 = 24 - 24 = 0
as D = 0, the given quadratic equation has real and equal roots
(vi) (x - 2a)(x - 2b) = 4ab
The given equation (x - 2a)(x - 2b) = 4ab can also be written as x2 - x(2a + 2b) and
c = 0[4ab - 4ab = 0 ]
D = b2 - 4ac
⇒ [-(2a + 2a)]2 - 4×1×0 = (2a + 2b)2 > 0
⇒ as equal root of any integers is always positive
⇒ D > 0, hence the discriminant of the equation is positive
(vii) 2(a2 + b2 )x2 + 2(a + b)x + 1 = 0
The given equation is 2(a2 + b2 )x2 + 2(a + b)x + 1 = 0
It is in the form of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here a = 2(a2 + b2 ), b = 2(a + b) and c = 1
∴ D = b2 - 4ac
⇒ (-2abcd)2 - 9×9a2b2 × 16c2d2
⇒ b + 6a2 b2 c2 d2 - 57a2 b2 c2 d2 = 0
Hence as D = 0, the equation as Real and equal roots
(viii) 2(a2 + b2 )x2 + 2(a + b)x + 1 = 0
The given equation is 2(a2 + b2 )x2 + 2(a + b)x + 1 = 0
It is in the farm of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here a = 2(a2 + b2 ), b = 2(a + b) and c = 1
∴ D = b2 - 4ac
⇒ [2(a + b)]2 - 4 × 2(a2 + b2 )×1
⇒ 4a2 + ab2 + 8ab - 8a2 - 8b2
⇒8ab + 4(a2 + b2 ) < 0
as D < 0, The discriminant is negative and the nature of the roots are not real
(ix) (b + c)x2 - (a + b + c)x + a = 0
The given equation is (b + c)x2 - (a + b +c)x + a = 0
Here a + b + c, b = -(a + b + c) and c = a
∴ D = b2 - 4ac
⇒ [ - (a + b + c)]2 - 4×(b+c)×a
⇒(a + b +c)2 - 4abc > 0
∴ as D > 0, the discriminant is positive and the nature of the roots are real and unequal
2. Find the values of k for which the roots are real and equal in each of the following equation:
(i) kx2 + 4x + 1 = 0
(ii) kx2 - 2√5x + 4 = 0
(iii) 3x2 - 5x + 2k = 0
(iv) 4x2 + kx + 9 = 0
(v) 2kx2 - 40x + 25 = 0
(vi) 9x2 - 24x + k = 0
(vii)4x2 - 3kx + 1 = 0
(viii) x2 - 2(5 + 2k)x + 3(7 + 10k) = 0
Solution
(i) kx2 + 4x + 1 = 0
The given equation kx2 + 4x + 1 = 0 is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0 where
a = k, b = 4, c = 1
given that, the equation has real and equal roots
(ii) kx2 - 2√5x + 4 = 0
The given equation kx2 - 2√5x + 4 = 0 is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0 where
a = k, b = -2√5 and c = 4
⇒ given that, the equation has real and equal roots
i.e., D = b2 - 4ac = 0
⇒ (-2√5)2 4 ×k ×4 = 0
⇒ 20 = 16k ⇒ k = 20/16 = 5/4 ∴ k = 5/4
∴ The value of k = 5/4
(iii) 3x2 - 5x + 2k = 0
The given equation is 3x2 - 5x + 2k = 0
This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here, a = 3, b = -5 and c = 2k
⇒given that, the equation has real and equal roots
i.e., D = b2 - 4ac = 0
⇒ (-5)2 - 4×3×(2k) = 0
⇒ 25 = 24k
⇒ k = 25/24
∴ The value of k = 25/24
(iv) 4x2 + kx + 9 = 0
The given equation is 4x2 + kx + 9 = 0
This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here, a = 4, b = k and c = 9
given that, the equation has real and equal roots
i.e., D = b2 - 4ac = 0
⇒ k2 - 4×4×9 = 0
⇒ k2 - 16×9
⇒ k = √(16×9) = 4×3 = 12
∴ The value of k = 12
(v) 2kx2 - 40x + 25 = 0
The given equation is 2kx2 - 40x + 25 = 0
This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here, a = 2k, b = -40 and c = 25
Given that, the equation has real and equal roots
I.e., D = b2 - 4ac = 0
⇒ (-10)2 - 4×2k ×25 = 0
⇒ 1600 - 200k = 0
⇒ k = 1600/200 = 8 ∴ k = 8
∴ The value of k = 8
(vi) 9x2 - 24x + k = 0
The given equation is 9x2 - 24x + k = 0
This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here, a = 9, b = -24, and c = k
given that, the nature of the roots of this equation is real and equal
i.e., D = b2 - 4ac = 0
⇒(-24)2 - 4×4×k = 0
⇒ 576 - 36k = 0
⇒ k = 576/36 = 16 ∴ k = 16
∴ The value of k = 16
(vii) 4x2 - 3kx + 1 = 0
The given equation is 4x2 - 3kx + 1 = 0
This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx +c = 0
Here, a = 4, b = -3k, and c = 1
given that, the nature of the roots of this equation is real and equal
i.e., D = b2 - 4ac = 0
⇒ D = b2 - 4ac = 0
⇒ (-3k)2 - 4×4×1 = 0
(viii) x2 - 2(5 + 2k)x + 3(7 + 10k) = 0
The given equation is x2 - 2(5 + 2k)x + 3(7 + 10k) = 0
Here, a = 1, b = -2(5+2k) and c = 3(7 + 10k)
given that, the nature of the roots of this equation are real and equal
i.e., D = b2 - 4ac = 0
(ix) (3k + 1)x2 + 2(k + 1)x + k = 0
The given equation is (3k + 1)x2 + 2(k + 1)x + k = 0
This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here a =3k + 1, b = 2(k + 1) and c = k
Given that the nature of the roots of this equation are real and equal
(x) kx2 + kx + 1 = -4x2 - x
The given equation is kx2 + kx + 1 = -4x2 - x bringing all the 'x' components to one side,
we get the equation as x2 (4 +k) + x(k + 1) + 1 = 0
This equation is in the form of the general quadratic equation i.e., ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here a = 4 + k, b = k + 1 and c = 1
given that the nature of the roots of the given equation are real and equal
Here a = k + 1, b = 2(k + 3) and c = k + 8
given that the nature of the roots of this equation are real and equal i.e.,
D = b2 - 4ac = 0

Here a = 1, b = -2k and c = 7k -12
given that the nature of the roots of this equation are real and equal i.e.,
D = b2 - 4ac = 0

It is in the form of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here, a = k +1, b = -2(3k + 1) and c = 8k +1)
given that the nature of the roots of the given equation are real and equal i.e.,
D = b2 - 4ac = 0

(xiv) 5x2 - 4x +2 +k(4x2 - 2x +1) = 0

This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here a = 4 - k, b = 2k + 4 and c = 8k + 1
given that the nature of the roots of this equation are real and equal i.e.,
D = b2 - 4ac = 0

This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here a = 2k + 1, b = 2(k + 3) and c = k + 5
given that the nature of the roots for this equation are real and equal i.e.,
D = b2 - 4ac = 0

(xvii) 4x2 - 2(k + 1)x + (k + 4) = 0
This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
here a = 4, b = -2(k + 1), c = k + 4
Given that the nature of the roots of this equation is real equal i.e. D = b2 - 4ac = 0

This equation is in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here a = 1, b = -2(k + 1) and c = k + 4
The nature of the roots of this equation is given that it is real and equal
i.e., O = b2 - 4ac = 0
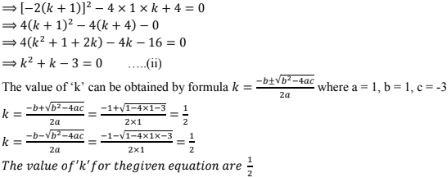
It is in the form of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here a = k2 , b = -2(2k - 1) and c = 4
Given that the nature of the roots of the equation are real and equal

(xx) (k + 1)x2 - 2(k - 1)x + 1 = 0
It is in the form of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0
Here a = k + 1, b = -2(k - 1) and c = 1
given that the nature of the roots for the equation are real and equal
i.e., D = b2 - 4ac = 0

It is in the form of the equation ax2 + bx +c = 0
Here a = 2, b = k, and c = 3
given that the roots of the equation are real and equal i.e., D = b2 - 4ac = 0

a = 6, b = - 2k, c = 6
given that the roots are real and equal

given that the roots are real and equal i.e.,
D = b2 - 4ac = 0
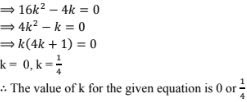
3. In the following determine the set of values of k foe which the green quadratic equation has real roots:
(ii) 2x2 + kx + 3 = 0
(iii) 2x2 - 5x - k = 0
(iv) kx2 + 6x +1 = 0
(v) x2 -kx + 9 = 0
given that the quadractic equation has real roots i.e., D = b2 - 4ac ≥ 0
Given here a = 2, b = 3, c = k
⇒ 9 - 4 ×2×k ≥ 0
⇒ 9 - 8k ≥ 0
⇒ 9 ≥ 8k
⇒ k ≤ 9/8
The value of k does not exceed 4/8 to have roots
given that the quadratic equation has real roots i.e., D = b2 - 4ac ≥ 0


Here a = k, b = 6, c = 1
given that the equation has real roots
i.e., D = b2 - 4ac ≥ 0

(v) x2 - kx + 9 = 0
Here a = 1, b = - k, c = 9
given that the equation has real roots

Here a = 2, b = k, c = 2
Given, that the equation has real roots

Here a = 3, b = 2, c = k
Given that the quadratic equation has real roots i.e., D= b2 - 4ac

Here a = 4, b = -3k, c = 1

Here a = 2, b = k, c = - 4


5. Find the least positive value of k for which the equation x2 + kx + 4 = 0 has real roots.

6. Find the value of k for which the gives quadratic equation has real and distinct roots


2b = a + c

a/b = c/d



either a = 0 or a3 + c3 = 3abc.









