RD Sharma Solutions Chapter 5 Trigonometric Ratios Exercise 5.3 Class 10 Maths

Chapter Name | RD Sharma Chapter 5 Trigonometric Ratios |
Book Name | RD Sharma Mathematics for Class 10 |
Other Exercises |
|
Related Study | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths |
Exercise 5.3 Solutions
Evaluate the following :
1. sin 20°/cos 70°
Solution

(ii) cos19°/sin71°
Solution
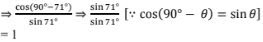
(iii) sin 21°/cos 69°
Solution
(iv) tan 10°/cot 80°
Solution
(v) sec 11°/cosec 79°
Solution
Evaluate the following :
2. (i) [sin 49°/cos 45°]2 + [cos 41°/sin 49°]
Solution

(ii) cos 48° - sin 42°
Solution
cos 48° = cos(90° - 42°) sin 42°
∴ sin 42° - sin 42° = 0
(iii) cot 40°/cos 35° - 1/2[ cos 35°/sin 55°]
Solution

(iv) [sin 27°/cos 63°] - [cos 63°/sin 27°]2
Solution

(v) tan 35°/ cot 55° + cot 63°/cos 63° - 1
Solution

(vi) sec 70°/cosec 20° + sin 59°/cos 31°
Solution
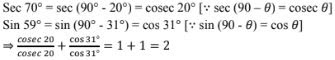
(vii) sec 50° sin 40° + cos 40° cosec 50°
Solution
sec 50° = sec (90° - 40°) = cosec 40°
cos 40° = cos(90° - 50°) = sin 50°
∴ sin θ cosec θ = 1
⇒ cosec 40° sin 40° + sin 50° cosec 50°
⇒ 1+ 1 = 2
3. Express each one of the following in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles lying between 0° and 45°
(i) sin 59° + cos 56°
Solution
sin 59° = sin (90° - 59°) = cos 31°
cos 56° = cos (65° - 34°) = sin 34°
⇒ cos 31° + sin 34°
(ii) tan 65° + cot 49°
Solution
tan 65° = tan(90° - 25°) = cot 5°
cot 49° = cot(90° - 41°) = tan 41°
⇒ cot 25° + tan 41°
(iii) sec 76° + cosec 52°
Solution
sec 76° = sec(90° - 14°) = cosec 14°
cosec 52° = cosec(90° - 88°) = sec 38°
⇒ cosec 14° + sec 38°
(iv) cos 78° + sec 78°
Solution
cos 78° = cos(90° - 12°) = sin 12°
sec 78° = sec(90° - 12°) = cosec 12°
⇒ sin 12° + cosec 12°
(v) cosec 54° + sin 72°
Solution
cosec 54° = cosec(90° - 36°) = sec 36°
sin 72° = sin(90° - 18°) = cos 18°
⇒ sec 36° + cos 18°
(vi) cot 85° + cos 75°
Solution
cot 85° = cot(90° - 5°) = tan 5°
cos 75° = cos(90° - 15°) = sin 15°
= tan 5° + sin 15°
(vii) sin 67° + cos 75°
Solution
sin 67° = sin(90° - 23°) = cos 23°
cos 75° = cos(90° - 15°) = sin 15°
= cos 23° + sin 15°
4. Express cos 75° + cot 75° in terms of angles between 0° and 30°.
Solution
cot 75° = cos(90° - 15°) = sin 15°
cot 75° = cot(90° - 15°) = tan 15°
= sin 15° + tan 15°
5. If sin3A = cos(A - 26°), where 3A is an acute angle, find the value of A = ?
Solution
Cos θ = sin (90° - θ)
⇒ cos(A - 26) = sin(90° - (A - 26°) ]
⇒ sin 3A = sin(90° - (A - 26°)]
Equating angles on both sides
3A = 90° - A + 26°
4A = 116°
A = 116°/4 = 29°
∴ A = 29°
6. If A, B, C are interior angles of a triangle ABC, prove that
(i) tan[(c + a)/2 = cot(B/2)
(ii) sin (B+C)/2 = cos A/2
Solution

7. Prove that
(i) tan 20° tan 35° tan 45° tan 55° tan 70° = 1
Solution
tan 20° = tan(90° - 70°) = cot 70°
tan 35° = tan(90° - 70°) = cot 55°
tan 45° = 1
⇒ cot 70° tan 70° × cot 55° tan 55° × tan 45° cot θ = tan θ = 1
⇒ 1 × 1 × 1 = 1
Hence proved.
(ii) sin 48° sec 42° + cosec 42° = 2
Solution
sin 48° = sin(90° - 42°) = cos 42°
cos 45° = cos(90° - 42°) = sin 42°
sec θ . cos θ = 1 . sin θ cosec θ = 1
⇒ cos 42° sec 42° + sin 42° cosec 42°
⇒ 1 + 1 = 2
∴ LHS = RHS
(iii) sin 70°/cos 20° + cosec 20°/sec 70° - 2 cos 70° cosec 20° = 0
Solution
sin(70°) = sin(90° - 20°) = cos 20°
cosec 20° = cosec(90° - 70°) = sec 70°
cos 70° = cos(90° - 20°) = sin 20°
⇒ cos 20°/cos 20° + sec 70°/sec 70° - 2 sin20° cosec 20°
1 + 1 - 2(1) = 0
∴ LHS = RHS
Hence proved
(iv) cos 80°/sin 10° + cos 59° cosec 31° = 2
Solution
cos 80° = cos(90° - 10°) = sin 10°
cos 59° = cos(90° - 31°) = sin 31°
⇒ sin 10°/sin 10° + sin 31° cosec 31°
= 1 + 1 = 2 [∵ sin θ cosec θ = 1]
Hence proved
8. Prove the following .
(i) sin θ sin(90 - θ) - cosθ cos(90 -θ) = 0
Solution
sin(90 - θ) = cos θ
cos(90 - θ) - cos θ sin θ = 0
∴ LHS = RHS
Hence proved
(ii) [cos(90° - θ) sec(90° - θ) tanθ]/[cosec(90° - θ) sin(90° - θ) cot(90° - θ) + tan(90° - θ)/cotθ = 2
Solution
cos(90° - θ) = sinA
cosec(90° - θ) = sec θ
sec(90° - θ) = cosec θ
sin(90° - θ) = cos θ
cot(90° - θ) = tan θ


tan 10° = tan(90° - 80°) = cot 80°
tan 20° = tan(90° - 70°) = cot 70°
⇒ cos(40° - θ) - cos(40° - θ) = cots 89° tan 89°. cot 80° cot 70° tan 70°
cot. tanθ = 1
= 1 . 1 . 1 = 1
LHS = RHS
Hence proved

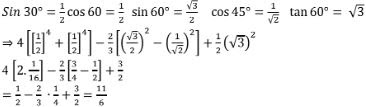

tan 40° = tan(90° - 50°) = cot 55°
tan 65° = 1
cot 55° tan 55° cot 50° tan 50° tan 45°
1 × 1× 1 = 1
tan(55° - θ) = cot(90° - (55° - θ) = cot(35° + θ)
⇒ sec(25° - θ) - sec(25° -θ) tan (55° - θ) + tan(55° - θ) = 0
⇒ tan 7° tan 23° tan 60° cot 23° tan 60°
1×1× √3 = √3
Cot 15° = tan(90° - 75°) = tan 75°
= 2 - 2/5 - 3/5 = 2 - 1 = 1



Cos θ = cos (90 - θ)
Cos (θ - 45°) = sin(90° - (θ - 45°)) = sin(90° - θ + 45°)
Sin θ = sin (135 - θ)
θ = 135 - θ
2θ = 135
∴ θ = 135/2
(i) Sin (B+C)/2 = cos A/2
(ii) cos (B+C)/2 = Sin A/2
B - C = 180 - A/2

Here 20 + 45° and 30 - θ° are acute angles:
Sin (2θ + 45°) = sin (90 - (30 - θ))
Sin(2θ + 45°) = sin (90° - 30 + θ)
On equating sin of angle of we get
2θ + 45 = 60 + θ
2θ - θ = 60 - 45
θ = 15°
Sec θ = sec (90 - 60°)
On equating we get
sec θ = sec 30°
θ = 30°

sin 2θ = cos 2θ
⇒ sin 4θ = sin(90 - 2θ)
⇒ 4θ = 90 - 2θ
⇒ 6θ = 90
⇒ θ = 90/6
⇒ θ = 15°
We know that sin(90 - θ) = cos θ
sin 3θ = sin(90 - (θ - 6°))
⇒ sin 3θ = sin(90 - θ + 6°)
⇒ sin 3θ = sin (96° - θ)
⇒ 3θ = 96° - θ
⇒ 4θ = 96°
⇒ θ = 24°
⇒ A = 110/5 = 22
⇒ 3A = 132/3
⇒ A = 44

