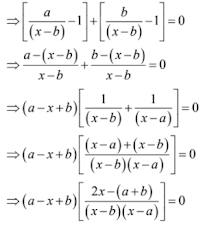RS Aggarwal Solutions Chapter 10 Quadratic Equation Exercise 10A Class 10 Maths
Chapter Name | RS Aggarwal Chapter 10 Quadratic Equation |
Book Name | RS Aggarwal Mathematics for Class 10 |
Other Exercises |
|
Related Study | NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths |
Exercise 10A Solutions
1. Which of the following are quadratic equation in x ?
(i) x2 – x + 2 = 0
(ii) 2x2 + 5/2x – 3 = 0
(iii) √2x2 + 7x + 5√2
(iv) 1/3x2 + 1/5x – 2 = 0
(v) x2 – 3x - √x + 4 = 0
(vi) x – 6/x = 3
(vii) x2 – 2/x = x2
(viii) x2 – 1/x2 = 5
(ix) (x + 2)3 = x3 – 8
(x) (2x + 3(3x + 2) = 6(x – 1)(x – 2)
(xi) (x + 1/x)2 = 2(x + 1/x) + 3
Solution
(i) (x2 – x + 3) is a quadratic polynomial
∴ x2 – x + 3 = 0 is a quadratic equation.
(ii) Clearly, (2x2 + 5/2.x - √3) is a quadratic polynomial.
∴ 2x2 + 5/2.x - √3 = 0 is a quadratic equation.
(iii) Clearly, (√2x2 + 7x + 5√2) is a quadratic polynomial.
√2x2 + 7x + 5√2 = 0 is a quadratic equation.
(iv) Clearly, (1/3x2 + 1/5.x – 2) is a quadratic polynomial.
∴ 1/3x2 + 1/5x – 2 = 0 is a quadratic equation.
(v) (x2 – 3x - √x + 4) contains a term with √x, i.e., x1/2, where 1/2 is not a integer.
Therefore, it is not a quadratic polynomial.
∴ x2 – 3x - √x + 4 = 0 is not a quadratic equation.
(vi) x – 6/x = 3
⇒ x2 – 6 = 3x
⇒ x2 – 3x – 6 = 0
(x3 – 3x – 6) is not quadratic polynomial; therefore, the given equation is quadratic.
(vii) x2 – 2/x = x2
⇒ x2 + 2 = x3
⇒ x3 – x2 – 2 = 0
(x3 – x2 – 2) = 0 is not a quadratic polynomial.
∴ x3 – x2 – 2 = 0 is not a quadratic equation.
(viii) x2 – 1/x2 = 5
⇒ x4 – 1 = 5x2
⇒ x4 – 5x2 – 1 = 0
(x4 – 5x2 - 1) is a polynomial with degree 4.
∴ x4 – 5x2 – 1 = 0 is not a quadratic equation.
(ix) (x + 2)3 = x3 – 8
⇒ x3 + 6x2 + 12x + 8 = x3 – 8
⇒ 6x2 + 12x + 16 = 0
This is of form ax2 + bx + c = 0
Hence, the given equation is a quadratic equation.
(x) (2x + 3)(3x + 2) = 6(x – 1)(x – 2)
⇒ 6x2 + 4x + 9x + 6 = 6(x2 – 3x + 2)
⇒ 6x2 + 13x + 6 = 6x2 – 18x + 12
⇒ 31x – 6 = 0
This is of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0
Hence, the given equation is not a quadratic equation.
(xi) (x + 1/x)2 = 2(x + 1/x) + 3
⇒ (x2 + 1)/x)2 = 2(x2 + 1)/x + 3
⇒ (x2 + 1)2 = 2x(x2 + 1) + 3x2
⇒ x4 + 2x2 + 1 = 2x3 + 2x + 3x2
⇒ x4 – 2x3 – x2 – 2x + 1 = 0
This is not of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0
Hence, the given equation is not a quadratic equation.
2. Which of the following are the roots of 3x2 + 2x – 1 = 0 = ?
(i) – 1
(ii) 1/3
(iii) – 1/2
Solution
The given equation is (3x2 + 2x – 1 = 0).
(i) x = (-1)
LHS = x2 + 2x – 1
= 3 × (-1)2 + 2 × (-1) – 1
= 3 – 2 – 1
= 0
= R.H.S.
Thus, (-1) is a root of (3x2 + 2x – 1 = 0).
(ii) On subtracting x = 1/3 in the given equation, we get:
L.H.S. = 3x2 + 2x – 1
= 3 × (1/3)2 + 2 × 1/3 – 1
= 3 × 1/9 + 2/3 – 1
= (1 + 2 – 3)/3
= 0/3
= 0
= R.H.S.
Thus, (1/3) is a root of (3x2 + 2x – 1 = 0)
(iii) On subtracting x = (-1/2) in the given equation, we get
L.H.S = 3x2 + 2x – 1
= 3 × (-1/2)2 + 2 × (-1/2) – 1
= 3 × 1/4 – 1 – 1
= 3/4 – 2
= (3 – 8)/4
= -5/4 ≠ 0
Thus, L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Hence, (-1/2) is a solution of (3x2 + 2x – 1 = 0).
3. Find the value of k for which x = 1 is a root of the equation x2 + kx + 3 = 0.
Solution
It is given that (x = 1) is a root of (x2 + kx + 3 = 0).
Therefore, (x = 1) must satisfy the equation.
⇒ (1)2 + k × 1 + 3 = 0
⇒ k + 4 = 0
⇒ k = - 4
Hence, the required value of k is -4.
4. Find the value of a and b for which x = 3/4 and x = - 2 are the roots of the equation ax2 + bx – 6 = 0
Solution
It is given that 3/4 is a root of ax3 + bx – 6 = 0; therefore, we have:
a × (3/4)2 + b × 3/4 - 6 = 0
⇒ 9a/16 + 3b/4 = 6
⇒ (9a + 12b)/16 = 6
⇒ 9a + 12b – 96 = 0
⇒ 3a + 4b = 32 ....(i)
Again, (-2) is a root of ax2 + bx – 6 = 0; therefore, we have:
a × (-2)2 + b × (-2) – 6 = 0
⇒ 4a – 2b = 6
⇒ 2a – b = 3 ....(ii)
On multiplying (ii) by 4 and adding the result with (i), we get:
⇒ 3a + 4b + 8a – 4b = 32 + 12
⇒ 11a = 44
⇒ a = 4
Putting the value of a in (ii), we get:
2 × 4 – b = 3
⇒ 8 – b = 3
⇒ b = 5
Hence, the required values of a and b are 4 and 5, respectively.
5. (2x – 3)(3x + 1) = 0
Solution
(2x – 3)(3x + 1) = 0
⇒ 2x – 3 = 0 or 3x + 1 = 0
⇒ 2x = 3 or 3x = - 1
⇒ x = 3/2 or x = - 1/3
Hence, the roots of the given equation are 3/2 and -1/3.
6. 4x2 + 5x = 0
Solution
4x2 + 5x = 0
⇒ x(4x + 5) = 0
⇒ x = 0 or 4x + 5 = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x = - 5/4
Hence, roots of the given equations are 0 and -5/4.
7. 3x2 – 243 = 0.
Solution
Given:
3x2 – 243 = 0
⇒ 3(x2 – 81) = 0
⇒ (x)2 – (9)2 = 0
⇒ (x + 9)(x – 9) = 0
⇒ x + 9 = 0 or x – 9 = 0
⇒ x = - 9 or x = 9
Hence, -9 and 9 are the roots of the equation 3x2 – 243 = 0.
8. 2x2 + x – 6 = 0
Solution
We write, x = 4x – 3 as 2x2 × (-6)
= -12x2
= 4x × (-3x)
∴ 2x2 + x – 6 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 4x – 3x – 6 = 0
⇒ 2x(x + 2) – 3(x + 2) = 0
⇒ (x + 2)(2x – 3) = 0
⇒ x + 2 = 0 or 2x – 3 = 0
⇒ x = - 2 or x = 3/2
Hence, the roots of the given equations are -2 and 3/2.
9. x2 + 6x + 5 = 0
Solution
We write, 6x = x + 5x as x2 × 5 = 5x2 = x × 5x
∴ x2 + 6x + 5 = 0
⇒ x2 + x – 5x + 5 = 0
⇒ x(x + 1) + 5(x + 1) = 0
⇒ (x + 1)(x + 5) = 0
⇒ x + 1 = 0 or x + 5 = 0
⇒ x = - 1 or x = - 5
Hence, the roots of the given equations are -1 and -5.
10. 9x2 – 3x – 2 = 0
Solution
We write, -3x = 3x – 6x as 9x2 × (-2)
= -18x2
= 3x × (-6x)
∴ 9x2 – 3x – 2 = 0
⇒ 9x2 + 3x – 6x – 2 = 0
⇒ 3x(3x + 1) – 2(3x + 1) = 0
⇒ (3x + 1)(3x – 2) = 0
⇒ 3x + 1 = 0 or 3x – 2 = 0
⇒ x = -1/3 or x = 2/3
Hence, the roots of the given equations are -1/3 and 2/3.
11. x2+ 12x + 35 = 0
Solution
x2 + 12 + 35 = 0
⇒ x2 + 7x + 5x + 35 = 0
⇒ x(x + 7) + 5(x + 7) = 0
⇒ (x + 5)(x + 7) = 0
⇒ x + 5 = 0 or x + 7 = 0
⇒ x = - 5 or x = - 7
Hence, -5 and -7 are the roots of the equation x2 + 12x + 35 = 0.
12. x2 = 18x – 77
Solution
x2 = 18x – 77
⇒ x2 – 18x + 77 = 0
⇒ x2 – (11x + 7x) + 77 = 0
⇒ x2 – 11x – 7x + 77 = 0
⇒ x(x – 11) – 7(x – 11) = 0
⇒ (x – 7)(x – 11) = 0
⇒ x – 7 = 0 or x – 11 = 0
⇒ x = 7 or x = 11
Hence, 7 and 11 are the roots of the equations x2 = 18x – 77.
13. 6x2+ 11x + 3 = 0.
Solution
Given:
6x2 + 11x + 3 = 0
⇒ 6x2 + 9x + 2x + 3 = 0
⇒ 3x(2x + 3) + 1(2x + 3) = 0
⇒ (3x + 1)(2x + 3) = 0
⇒ 3x + 1 = 0 or 2x + 3 = 0
⇒ x = -1/3 or x = -3/2
Hence, -1/3 and -3/2 are the roots of the equation 6x2 + 11x + 3 = 0
14. 6x2+ x – 12 = 0.
Solution
Given:
6x2 + x – 12 = 0
⇒ 6x2 + 9x – 8x – 12 = 0
⇒ 3x(2x + 3) – 4(2x + 3) = 0
⇒ (3x – 4)(2x + 3) = 0
⇒ 3x – 4 = 0 or 2x + 3 = 0
⇒ x = 4/3 or x = -3/2
Hence, 4/3 and -3/2 are the roots of the equation 6x2 + x – 12 = 0.
15. 3x2 – 2x – 1 = 0
Solution
We write, -2x = -3x + x as 3x2 × (-1)
= -3x2
= (-3x) × x
∴ 3x2 – 2x – 1 = 0
⇒ 3x(x – 1) + 1(x – 1) = 0
⇒ (x – 1)(3x + 1) = 0
⇒ x – 1 = 0 or 3x + 1 = 0
⇒ x = 1 or x = -1/3
Hence, the roots of the given equation are 1 and – 1/3.
16. 4x2 – 9x = 100
Solution
Given:
4x2 – 9x = 100
⇒ 4x2 – 9x – 100 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – (25x – 16x) – 100 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – 25x + 16x – 100 = 0
⇒ x(4x – 25) + 4(4x – 25) = 0
⇒ (4x – 25)(x + 4) = 0
⇒ 4x – 25 = 0 x + 4 = 0
⇒ x = 25/4 or x = -4
Hence, the roots of the equation are 25/4 and -4.
17. 15x2 – 28 = x
Solution
Given:
15x2 – 28 = x
⇒ 15x2 – x – 28 = 0
⇒ 15x2 – (21x – 20x) – 28 = 0
⇒ 15x2 – 21x + 20x – 28 = 0
⇒ 3x(5x – 7) + 4(5x – 7) = 0
⇒ (3x + 4)(5x – 7) = 0
⇒ 3x + 4 = 0 or 5x – 7 = 0
⇒ x = -4/3 or x = 7/5
Hence, the roots of the equation are -4/3 and 7/5.
18. 4 – 11x = 3x2
Solution
Given:
4 – 11x = 3x2
⇒ 3x2 + 11x – 4 = 0
⇒ 3x2 + 12x – x – 4 = 0
⇒ 3x(x + 4) - 1(x + 4) = 0
⇒ (x + 4)(3x – 1) = 0
⇒ x + 4 = 0 or 3x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = -4 or x = 1/3.
19. 48x2 - 13x – 1 = 0
Solution
48x2 – 13x – 1 = 0
⇒ 48x2 – (16x – 3x) – 1 = 0
⇒ 48x2 – 16x + 3x – 1 = 0
⇒ 16x(3x – 1) + 1(3x – 1) = 0
⇒ (16x + 1)(3x – 1) = 0
⇒ 16x + 1 = 0 or 3x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = -1/16 or x = 1/3
Hence, the roots of equation are -1/16 and 1/3.
20. x2 + 2√2x – 6 = 0
Solution
2√2x = 3√2x - √2x as x2 × (-6)
= - 6x2
= 3√2x × (-√2x)
∴ x2 + 2√2x – 6 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2√2x - √2x – 6 = 0
⇒ x(x + 3√2) - √2(x + 3√2) = 0
⇒ (x + 3√2)(x - √2) = 0
⇒ x + 3√2 = 0 or x - √2 = 0
⇒ x = -3√2 or x = √2
Hence, the roots of the given equation are -3√2 and √2
21. √3x2 + 10x + 7√3 = 0
Solution
We write: 10x = 3x + 7x as √3x2 × 7√3
= 21x3
= 3x × 7x
∴ √3x2 + 10x + 7√3 = 0
⇒ √3x2 + 3x + 7x + 7√3 = 0
⇒ √3x(x + √3) + 7(x + √3) = 0
⇒ (x + √3)(√3x + 7) = 0
⇒ x + √3 = 0 or √3x + 7 = 0
⇒ x = -√3 or x = -7/√3 = -(7√3)/3
Hence, the roots of the given equation are -√3 and (-7√3)/3.
22.√3x2 + 11x + 6√3 = 0
Solution
√3x2 + 11x + 6√3 = 0
⇒ √3x2 + 9x + 2x + 6√3 = 0
⇒ √3x(x + 3√3) + 2(x + 3√3) = 0
⇒ (x + 3√3)(√3x + 2) = 0
⇒ x + 3√3 = 0 or √3x + 2 = 0
⇒ x = -3√3 or x = -2/√3
= (-2 × √3)/(√3 × √3)
= -2√3/3
Hence, the roots of the equation are -3√3 and (-2√3)/3.
23. 3√3 + 4x - √7 = 0
Solution
Given:
3√7x2 + 4x - √7 = 0
⇒ 3√7x2 + 7x – 3x - √7 = 0
⇒ √7x(3x + √7) – 1(3x + √7) = 0
⇒ (3x + √7)(√7 – 1) = 0
⇒ 3x + √7 = 0 or √7x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = -√7/3 or x = 1√7 = (1 × √7)/(√7 × √7)
= √7/7
Hence, the roots of the equations are -√7/3 and √7/7.
24. √7x2 – 6x - 13√7 = 0
Solution
We write, -6x = 7x – 13 as √7x2 × (-13√7)
= -91x2
= 7x × (-13x)
∴ √7x2 + 7x – 13x - 13√7 = 0
⇒ √7x2 + 7x – 13x - 13√7 = 0
⇒ √7x(x + √7) – 13(x + √7) = 0
⇒ (x + √7)(√7x – 13) = 0
⇒ x + √7 = 0 or √7x – 13 = 0
⇒ x = -√7 or x = 13/√7
= (13√7)/7
Hence, the roots of the given equation are - √7 and 13√7/7
25. 4√6x2 – 13x - 2√6 = 0
Solution
4√6x2 – 13x - 2√6 = 0
⇒ 4√6x2 – 16x + 3x - 2√6 = 0
⇒ 4√2x (√3x - 2√2) + √3(√3x - 2√2) = 0
⇒ (4√2x + √3)(√3x - 2√2) = 0
⇒ 4√2x + √3 = 0 or √3x - 2√2 = 0
⇒ x = -√3/(4√2)
= (-√3 × √2)/(4√2 × √2)
= -√8/8
or x = 2√2/√3
= (2√2 × √3)/(√3 × √3)
= (2√6)/3
Hence, the roots of the equations are -√6/8 and 2√6/3.
26. 3x2 - 2√6x + 2 = 0
Solution
We write, -2√6x
= -√6x and 3x2 × 2
= 6x2
= (-√6x) × (-√6x)
∴ 3x2 - 2√6x + 2 = 0
⇒ 3x2 - √6x - √6x + 2 = 0
⇒ √3x(√3x - √2) - √2(√3x - √2) = 0
⇒ (√3x - √2)(√3x - √2) = 0
⇒ (√3x - √2)2 = 0
⇒ √3x - √2 = 0
⇒ x = √2/√3 = √6/3
Hence, √6/3 vis the repeated root of the given equation.
27. √3x2 - 2√2x - 2√3 = 0
Solution
We write, -2√2x
= -3√2x + √2x as √3x2 × (-2√3)
= -6x2
= (-3√2x) × (√2x)
∴ √3x2 - 2√2x - 2√3 = 0
⇒ √3x2 - 3√2x + √2x - 2√3 = 0
⇒ √3x(x - √6) + √2(x - √6) = 0
⇒ (x - √6)( √3x + √2) = 0
⇒ x - √6 = 0 or √3x + √2 = 0
⇒ x - √6 = 0 or x = - √2/√3
= -√6/3
Hence, the roots of the given equation are √6 and -√6/3.
28. x2 - 3√5x + 10 = 0
Solution
We write, -3√5x
= -2√5x - √5x as x2 × 10 = 10x2
= (-2√5x) × (-√5x)
∴ x2 - 3√5x + 10 = 0
⇒ x2 - 2√5x - √5x + 10 = 0
⇒ x(x - 2√5) - √5(x - 2√5) = 0
⇒ (x - 2√5)(x - √5) = 0
⇒ x(x - 2√5) - √5(x - 2√5) = 0
Hence, the roots of the given equations are √5 and 2√5.
29. x2 – (√3 + 1)x + √3 = 0
Solution
x2 – (√3x + 1)x + √3 = 0
⇒ x2 - √3x – x + √3 = 0
⇒ x(x - √3) – 1(x - √3) = 0
⇒ (x - √3)(x – 1) = 0
⇒ x - √3 = 0 or x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = √3 or x = 1
Hence, 1 and √3 are the roots of the given equations.
30. x2 + 3√3x – 30 = 0
Solution
We write, 3√3x = 5√3x - 2√3x as x2 × (-30)
= -30x2
= 5√3x × (-2√3)x
∴ x2 + 3√3x – 30 = 0
⇒ x2 + 5√3x - 2√3x – 30 = 0
⇒ x(x + 5√3) - 2√3(x + 5√3) = 0
⇒ (x + 5√3)(x - 2√3) = 0
⇒ x + 5√3 = 0 or x - 2√3 = 0
⇒ x = -5/√3 or x = 2√3
Hence, the roots of the given equation are -5√3 and 2√3.
31. √2x2 + 7x + 5√2 = 0
Solution
We write, 7x = 5x + 2x as √2x2 × 5√2
= 10x2
= 5x × 2x
∴ √2x2 + 7x + 5√2 = 0
⇒ √2x2 + 5x + 2x + 5√2 = 0
⇒ x(√2x + 5) + √2(√2x + 5) = 0
⇒ (√2x + 5)(x + √2) = 0
⇒ x + √2 = 0 or √2x + 5 = 0
⇒ x = -√2 or x = -(5/√2) = -(5√2)/2
Hence, the roots of the given equation are -√2 and -(5√2)/2.
32. 5x2 + 13x + 8 = 0
Solution
We write, 13x = 5x + 8x as 5x2 × 8
= 40x2
= 5x × 8x
∴ 5x2 + 13x + 8 = 0
⇒ 5x2 + 5x + 8x + 8 = 0
⇒ 5x(x + 1) + 8(x +1) = 0
⇒ (x + 1)(5x + 8) = 0
⇒ x + 1 = 0 or 5x + 8 = 0
x = -1 or x = - (8/5)
Hence, -1 and -8/5 are the roots of the given equation.
33. x2 – (1 + √2)x + √2 = 0
Solution
Given:
x2 – (1 + √2)x + √2 = 0
⇒ x2 – x - √2x + √2 = 0
⇒ x(x – 1) - √2(x – 1) = 0
⇒ (x - √2)(x – 1) = 0
⇒ x - √2 = 0 or x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = √2 or x = 1
Hence, the roots of the equation are √2 and 1.
34. 9x2 + 6x + 1 = 0
Solution
9x2 + 6x + 1 = 0
⇒ 9x2 + 3x + 3x + 1 = 0
⇒ 3x(3x + 1) + 1(3x + 1) = 0
⇒ (3x + 1)(3x + 1) = 0
⇒ 3x + 1 = 0 or 3x + 1 = 0
⇒ x = -1/3 or x = -1/3
Hence, -1/3 is the root of the equation 9x2 + 6x + 1 = 0.
35. 100x2 – 20x + 1 = 0
Solution
We write, -20x = -10x – 10x as 100x2 × 1
= 100x2
= (-10x) × (-10x)
∴ 100x2 – 20x + 1 = 0
⇒ 100x2 – 10x – 10x + 1 = 0
⇒ 10x(10x – 1) - 1(10x – 1) = 0
⇒ (10x – 1)(10x – 1) = 0
⇒ (10x – 1)2 = 0
⇒ 10x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = 1/10
Hence, 1/10 is the repeated root of the given equation.
36. 2x2 – x + 1/8 = 0
Solution
We write, -x = -x/2 – x/2 as 2x2
× 1/8
= x2/4
= - (x/2) × - (x/2)
2x2 –
x + 1/8 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – x/2 – x/2 + 1/8 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 1/4) – 1/2(x – 1/4) = 0
⇒ (x – 1/4)(2x – 1/2) = 0
⇒ x – 1/4 = 0 or 2x – 1/2 = 0
⇒ x = 1/4 or x = 1/4
Hence, 1/4 is the repeated root
of the given equation.
37. 10x – 1/x = 3
Solution
Given:
10x - 1/x = 3
⇒ 10x2 – 1 = 3x [Multiplying both
sides by x]
⇒ 10x2 – 3x – 1 = 0
⇒ 10x2 – (5x – 2x) – 1 = 0
⇒ 10x2 – 5x + 2x – 1 = 0
⇒ 5x(2x – 1) + 1(2x – 1) = 0
⇒ (2x – 1)(5x + 1) = 0
⇒ 2x – 1 = 0 or 5x + 1 = 0
⇒ x = 1/2 or x = -1/5
Hence, the roots of the equation are 1/2 and -1/5.
38. 2/x2 - 5/x + 2 = 0
Solution
Given:
2/x2 – 5/x + 2 = 0
⇒ 2 – 5x + 2x2 = 0 [Multiplying both sides by x2]
⇒ 2x2 – 5x + 2 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – (4x + x) + 2 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 4x – x + 2 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 2) – 1(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (2x – 1)(x – 2) = 0
⇒ 2x – 1 = 0 or x – 2 = 0
⇒ x = 1/2 or x = 2
Hence, the roots of the equation
are 1/2 and 2.
39. 2x2 + ax – a2
= 0
Solution
We write, ax = 2ax – ax as 2x2
× (- a2)
= -2a2x2
= 2ax × (- ax)
∴ 2x2 + ax – a2 = 0
⇒ 2x(x + a) – a(x + a)
=- 0
⇒ (x + a)(2x – a) = 0
⇒ x + a = 0 or 2x – a = 0
⇒ x = -a or x = a/2
Hence, -a and a/2 are the roots of the given equation.
40. x2+ 4bx – (a2 – b2) = 0
Solution
We write, 4bx = 2(a + b)x – 2(a – b)x as
4x2 × [-(a2 – b2)]
= -4(a2 – b2)x2
= 2(a + b)x × [-2(a – b)x]
∴ 4x2 + 4bx – (a2 - b2) = 0
⇒ 4x2 + 2(a + b)x – 2(a – b)x – (a – b)(a + b) = 0
⇒ 2x[2x + (a + b) – (a – b)[2x + (a + b)] = 0
⇒ [2x + (a + b)][2x – (a – b)] = 0
⇒ 2x + (a + b) = 0 or 2x – (a – b) = 0
⇒ x = -(a + b)/2 or x = (a – b)/2
Hence, -(a + b)/2 or x = (a – b)/2 are the roots of the given equation.
41. 4x2 - 4a2x + (a4 – b4) = 0
Solution
We write, -4a2x = -2(a2 + b2)x – 2(a2 – b2)x as
4x2 × (a4 – b4) = 4(a4 – b4)x2
= [-2(a2 + b2)]x × [-2(a2 – b2)]x
∴ 4x2 – 4a2x + (a4 – b4) = 0
⇒ 4x2 – 2(a2 + b2)x – 2(a2 – b2)x2 = [-2(a2 + b2)]x × [-2(a2 – b2)]x
⇒ 2x[2x – (a2 + b2)] – (a2 – b2)[2x – (a2 + b2)] = 0
⇒ [2x – (a2 + b2)] [2x – (a2 – b2)] = 0
⇒ 2x – (a2 + b2) = 0 or 2x – (a2 – b2) = 0
⇒ x = (a2 + b2)/2 or (a2 – b2)/2
Hence, (a2 + b2)/2 and (a2 – b2)/2 are the roots of the given equation.
42. x2 + 5x – (a2 + a – 6) = 0
Solution
We write, 5x = (a + 3)x – (a – 2)x as
x × [-(a2 + a – 6)]
= -(a2 + a – 6)x2
= (a + 3)x × [-(a – 2)x]
∴ x2 + 5x – (a2 + a – 6) = 0
⇒ x2 + (a + 3)x – (a – 2)x –(a + 3)(a – 2) = 0
⇒ x[x + (a + 3)] – (a – 2)[x + (a + 3)] = 0
⇒ [x + (a + 3)][x – (a – 2)] = 0
⇒ x + (a + 3) = 0, x - (a – 2) = 0
⇒ x = -(a + 3) or x = a – 2
Hence, -(a + 3) and (a – 2) are the roots of the given equation.
43. x2 – 2ax - (4b2 – a2) = 0
Solution
We have, -2ax = (2b – a)x – (2b + a)x as
x2 × [-(4b2 – a2)]
= -(4b2 – a2)x2
= (2b – a)x × [-(2b + a)x]
∴ x2 – 2ax – (4b2 – a2) = 0
⇒ x2 + (2b – a)x – (2b + a)x – (2b – a)(2b + a) = 0
⇒ x[x + (2b – a)] – (2b + a)[x + (2b – a)] = 0
⇒ [x + (2b – a)][x – (2b + a)] = 0
⇒ x + (2b – a) = 0 or x – (2b + a) = 0
x = -(2b – a) or x = 2b + a
⇒ x = a – 2b or x = a + 2b
Hence, a – 2b and a + 2b are the roots of the given equation.
44. x2 – (2b – 1)x + (b2 – b – 20) = 0
Solution
We write, -(2b – 1)x = -(b – 5)x – (b + 4)x as
x2 × (b2 – b – 20) = (b2 – b – 20)x2
= [-(b – 5)x] × [-(b + 4)x]
∴ x2 – (2b – 1)x + (b2 – b – 20) = 0
⇒ x2 – (b – 5)x – (b + 4)x + (b – 5)(b + 4) = 0
⇒ x[x – (b – 5)] – (b + 4)[x – (b – 5)] = 0
⇒ [x – b – 5]9x + (b + 4)] = 0
⇒ x – (b – 5) = 0 or x – (b + 4) = 0
⇒ x = b – 5 or x = b + 4
Hence, b – 5 and b + 4 are the roots of the given equation.
45. x2 + 6x - (a2 + 2a – 8) = 0
Solution
We write, 6x = (a + 4)x – (a – 2)x as
x2 × [-(a2 + 2a – 8)] = -(a2 + 2a – 8)x2
= (a + 4)x × [-(a – 2)x]
∴ x2 + 6x – (a2 + 2a – 8) = 0
⇒ x2 + (a + 4)x – (a – 2)x – (a + 4)(a – 2) = 0
⇒ x[x + (a + 4)] – (a – 2)[x + (a = 4)] = 0
⇒ [x + (a + 4)][x – (a – 2)] = 0
⇒ x + (a + 4) = 0 or x – (a – 2) = 0
⇒ x = - (a + 4) = 0 x = a – 2
Hence, -(a + 4) and (a – 2) are the roots of the given equation.
46. abx2 + (b2 – ac)x – bc = 0
Solution
abx2 + (b2 – ac)x – bc = 0
⇒ abx2 + b2x – acx – bc = 0
⇒ bx(ax + b) – c(ax + b) = 0
⇒ (bx – c) (ax + b) = 0
⇒ bx – c = 0 or ax + b = 0
⇒ x = c/b or x = -b/a
Hence, the roots of the equation are c/b and -b/a.
47. x2 – 4ax – b2 + 4a2 = 0
Solution
We write, -4ax = -(b + 2a)x + (b – 2a)x as
x2 × (-b2 + 4a2) = (-b2 + 4a2)x2
= -(b + 2a)x × (b – 2a)x
∴ x2 – 4ax – b2 + 4a2 = 0
⇒ x2 – (b + 2a)x(b – 2a)x – (b – 2a)(b + 2a) = 0
⇒ x[x – (b + 2a)] + (b – 2a)[x – (b + 2a)] = 0
⇒ [x – (b + 2a)][x + (b – 2a)] = 0
⇒ x – (b + 2a) = 0 or x + (b – 2a) = 0
⇒ x = 2a + b or x = -(b – 2a)
⇒ x = 2a + b or x = 2a – b
Hence, (2a + b) and (2a – b) are the roots of the given equation.
48. 4x2 – 2(a2 + b2)x + a2b2 = 0
Solution
4x2 – 2(a2 + b2)x + a2b2 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – 2a2x – 2b2x + a2b2 = 0
⇒ 2x(2x – a2) – b2(2x – a2) = 0
⇒ (2x – b2)(2x – a2) = 0
⇒ 2x – b2 = 0 or 2x – a2 = 0
⇒ x = b2/2 or x = a2/a
Hence, the roots of equation are b2/2 and a2/2.
49. 12abx2– (9a2 – 8b2)x – 6ab = 0
Solution
Given:
12abx2 – (9a2 – 8b2)x – 6ab = 0
⇒ 12abx2 – 9a2x + 8b2x – 6ab = 0
⇒ 3ax(4bx – 3a) + 2b(4bx – 3a) = 0
⇒ (3ax + 2b)(4bx - 3a) = 0
⇒ 3ax + 2b = 0 or 4bx – 3a = 0
⇒ x = -2b/3a or x = 3a/4b
Hence, the roots of the equation are -2b/3a and 3a/4b.
50. a2b2x2+ b2x – a2x – 1 = 0.
Solution
Given:
a2b2x + b2x – a2x – 1 = 0
⇒ b2x(a2x + 1) – 1(a2x + 1) = 0
⇒ (b2x – 1)(a2x + 1) = 0
⇒ (b2x – 1) = 0 or (a2x + 1) = 0
⇒ x = 1/b2 and -1/a2 are the roots of the given equation.
51. 9x2– 9(a + b)x + (2a2+ 5ab + 2b2) = 0
Solution
We write, -9(a + b)x = -3(2a + b)x – 3(a + 2b)x as
9x2 × (2a2 + 5ab + 2b2)
= 9(2a2 + 5ab + 2b2)x2
= [-3(2a + b)x] × [-3(a + 2b)x]
∴ 9x2 – 9(a + b)x + (2a2 + 5ab + 2b2) = 0
⇒ 9x2 – 3(2a + b)x – 3(a + 2b)x + (2a + b)(a + 2b) = 0
⇒ 3x[3x – (2a + b)] – (a + 2b)[3x – (2a + b)] = 0
⇒ [3x – (2a + b)][3x – (a + 2b)] = 0
⇒ 3x – (2a + b) = 0 or 3x – (a + 2b) = 0
⇒ x = (2a + b)/3 or x = (a + 2b)/3
Hence, (2a + b)/3 and (a + 2b)/3 are the roots of the given equation.
52. 16/x – 1 = 15/(x + 1), x ≠ 0 , -1
Solution
16/x – 1 = 15/(x + 1), x 4≠ 0, 1
⇒ 16/x – 1 = 15/(x + 1) = 1
⇒ (16x + 16 – 15x)/x(x + 1) = 1
⇒ (x + 16)/(x2 + x) = 1
⇒ x2 + x = x + 16 (Cross multiplication)
⇒ x2 – 16 = 0
⇒ (x + 4)(x – 4) = 0
⇒ x + 4 = 0 or x – 4 =0
⇒ x = -4 or x = 4
Hence, -4 and 4 are the roots of the given equation.
53. 4/x – 3 = 5/(2x + 3), x ≠ 0, -(3/2)
Solution
4/x – 3 = 5/(2x + 3), x ≠ 0, -(3/2)
⇒ 4/x – 5/(2x + 3) = 3
⇒ (8x + 12 – 5x)/x(2x + 3) = 3
⇒ (3x + 12)/(2x2 + 3x) = 3
⇒ (x + 4)/(2x2 + 3x) = 1
⇒ 2x2 + 3x = x + 4 (Cross multiplication)
⇒ 2x2 + 2x – 4 = 0
⇒ x2 + x – 2 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2x – x – 2 = 0
⇒ x(x + 2) – 1(x + 2) = 0
⇒ (x + 2)(x – 1) = 0
⇒ x + 2 = 0 or x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = -2 or x = 1
Hence, -2 and 1 are the roots of the given equation.
54. 3/(x + 1) - 1/2 = 2/(3x - 1), x = -1, 1/3
Solution
3/(x + 1) - 1/2 = 2/(3x - 1), x ≠ -1, 1/3
⇒ 3/(x + 1) – 2/(3x – 1) = 1/2
⇒ (9x – 3 – 2x – 2)/(x + 1)(3x – 1) = ½
⇒ (7x – 5)/(3x2 + 2x – 1) = 1/2
⇒ 3x2 + 2x – 1 = 14x – 10 (Cross multiplication)
⇒ 3x2 – 12x + 9 = 0
⇒ x2 – 4x + 3 = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x – x + 3 = 0
⇒ x(x – 3) – 1(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (x – 3)(x – 1) = 0
⇒ x – 3 = 0 or x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = 3 or x = 1
Hence, 1 and 3 are the roots of the given equation.
55. 1/(x – 1) – 1/(x + 5) = 6/7, x ≠ 1, -5
Solution
1/(x – 1) – 1/(x + 5) = 6/7, x ≠ 1, -5
⇒ (x + 5 – x + 1)/(x – 1)(x + 5) = 6/7
⇒ 6/(x2 + 4x – 5) = 6/7
⇒ x2 + 4x – 5 = 7
⇒ x2 + 4x – 12 = 0
⇒ x2 + 6x – 2x – 12 = 0
⇒ x(x + 6) – 2(x + 6) = 0
⇒ (x + 6)(x – 2) = 0
⇒ x + 6 = 0 or x – 2 = 0
⇒ x = -6 or x = 2
Hence, -6 and 2 are the roots of the given equation.
56. 1/(2a + b + 2x) = 1/2a + 1/b + 1/2x
Solution
1/(2a + b + 2x) = 1/2a + 1/b + 1/2x
⇒ 1/2a + b + 2x) – 1/2x = 1/2a + 1/b
⇒ (2x – 2a – b – 2x)/(2x(2a + b + 2x) = (2a + b)/2ab
⇒ -(2a + b)/(4x2 + 4ax + 2bx) = (2a + b)/2ab
⇒ 4x2 + 4ax + 2bx = -2ab
⇒ 4x2 + 4ax + 2bx = -2ab
⇒ 4x2 + 4ax + 2bx + 2ab = 0
⇒ 4x(x + a) + 2b(x + a) = 0
(x + a)(4x + 2b) = 0
⇒ x + a(4x + 2b) = 0
⇒ x + a = 0 or 4x + 2b = 0
⇒ x = -a or x = -(b/2)
Hence, -a and -(b/2) are the roots of the given equation.
57. (x + 3)/(x – 2) - (1 – x)/x = 4.1/4 , x ≠ 2, 0
Solution
Given:
(x + 3)/(x – 2) – (1 – x)/x = 17/4
⇒ [x(x + 3) – (1 – x)(x – 2)]/[(x – 2)x] = 17/4
⇒ [x2 + 3x – (x – 2 – x2 + 2x)]/(x2 – 2x) = 17/4
⇒ (x2 + 3x + x2 – 3x + 2)/(x2 – 2x) = 17/4
⇒ (2x2 + 2)/(x2 – 2x) = 17/4
⇒ 8x2 + 8 = 17x2 – 34x
⇒ -9x2 + 34x – 8 = 0
⇒ 9x2 – 34x – 8 = 0
⇒ 9x2 – 36x +2x – 8 = 0
⇒ 9x(x – 4) + 2(x – 4) = 0
⇒ (x – 4)(9x + 2) = 0
⇒ x – 4 = 0 or 9x + 2 = 0 ≠
⇒ x = 4 or x = -2/9
Hence, the roots of the equation are 4 and -2/9.
58. (3x – 4)/7 + 7/(3x – 4) = 5/2, x ≠ 4/3
Solution
(3x – 4)/7 + 7/(3x – 4) = 5/2, x ≠ 4/3
⇒ (3x – 4)2 + 49/7(3x – 4) = 5/2
⇒ 9x2 – 24x + 16 + 49)/(21x – 28) = 5/2
⇒ 18x2 – 48x + 130 = 105x – 140
⇒ 18x2 – 153x + 270 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 17x + 30 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 12x – 5x + 30 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 6) – 5(x – 6) = 0
⇒ (x – 6)(2x – 5) = 0
⇒ x – 6 = 0 or 2x – 5 = 0
⇒ x = 6 or x = 5/2
Hence, 6 and 5/2 are the roots of the given equation.
59. x/(x – 1) + (x – 1)/x = 4.1/4, x ≠ 0, 1
Solution
x/(x – 1) + (x – 1)/x = 4.1/4, x ≠ 0, 1
⇒ x2 + (x – 1)2/(x(x – 1)) = 17/4
⇒ (x2 + x2 – 2x + 1)/(x3 – x) = 17/4
⇒ (2x2 – 2x + 1)/(x2 – 1) = 17/4
⇒ 8x2 – 8x + 4 = 17x2 – 17x
⇒ 9x2 – 9x – 4 = 0
⇒ 9x2 – 12x + 3x – 4 = 0
⇒ 3x(3x – 4) + 1(3x – 4) = 0
⇒ (3x – 4)(3x + 1) = 0
⇒ (3x – 4)(3x + 1) = 0
⇒ 3x – 4 = 0 or 3x + 1 = 0
⇒ x = 4/3 or x = -(1/3)
Hence, 4/3 and -1/3 are the roots of the given equation.
60. x/(x + 1) + (x + 1)/x = 2.4/15, x ≠ 0, -1
Solution
x/(x +1) + (x + 1)/x = 2.4/15, x ≠ 0, -1
⇒ x2 + (x + 1)2/x(x + 1) = 34/15
⇒ (x2 + x2 + 2x + 1)/(x2 + x) = 34/15
⇒ (2x2 + 2x + 1)/(x2 + 1) = 34/15
⇒ 30x2 + 30x + 15 = 34x2 + 34x
⇒ 4x2 + 4x – 15 = 0
⇒ 4x2 + 10x – 6x – 15x = 0
⇒ 2x(2x + 5) – 3(2x + 5) = 0
⇒ (2x + 5)(2x – 3) = 0
⇒ 2x + 5 = 0 or 2x – 3 = 0
⇒ x = -5/2 or 2x – 3 = 0
Hence, -5/2 and 3/2 are the roots of the given equation.
61. (x – 4)/(x – 5) + (x – 6)/(x – 7) = 3.1/3, x ≠ 5, 7
Solution
(x – 4)/(x – 5) + (x – 6)/(x – 7) = 3.1/3, x ≠5, 7
⇒ (x – 4)(x – 7) + (x – 5)(x – 6)/{(x – 5)(x – 7)} = 10/3
⇒ (x2 – 11x + 28 + x2 – 11x + 30)/(x2 – 12x + 35) = 10/3
⇒ (2x2 – 22x + 58)/(x2 – 12x + 35) = 10/3
⇒ (x2 – 11x + 29)/(x2 – 12x + 35) = 5/3
⇒ 3x2 – 33x + 87 = 5x2 – 60x + 175
⇒ 2x2 – 33x + 87 = 5x2 – 60x + 175
⇒ 2x2 – 27x + 88 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 16x – 11x + 88 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 8) – 11(x – 8) = 0
⇒ (x – 8)(2x – 11) = 0
⇒ x – 8 = 0 or 2x – 11 = 0
⇒ x = 8 or x = 11/2
Hence, 8 and 11/2 are the roots of the given equation.
62. (x – 1)/(x – 2) + (x – 3)/(x – 4) = 3.1/3, x ≠ 2, 4
Solution
(x – 1)/(x – 2) + (x – 3)/(x – 4) = 3.1/3, x ≠ 2, 4
⇒ (x – 1)(x – 4) + (x – 2)(x – 3)}/{(x – 2)(x – 4) = 10/3
⇒ (x2 – 5x + 4 + x2 – 5x + 6)/(x2 – 6x + 8) = 10/3
⇒ (2x2 – 10x + 10)/(x2 – 6x + 8) = 10/3
⇒ (x2 – 5x + 5)/(x2 – 6x + 8) = 5/3
⇒ 3x2 – 15x + 15 = 5x2 – 30x + 40
⇒ 2x2 – 15x + 25 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 10x – 5x + 25 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 5) – 5(x – 5) = 0
⇒ (x – 5)(2x – 5) = 0
⇒ x – 5 = 0 or 2x – 5 = 0
⇒ x = 5 or x = 5/2
Hence, 5 and 5/2 are the roots of the given equation.
63. 1/(x – 2) + 2/(x – 1) = 6/x, x ≠ 0, 1, 2
Solution
1/(x – 2) + 2/(x – 1) = 6/x
⇒ (x – 1) + 2(x – 2)/(x – 1)(x – 2) = 6/x
⇒ (3x – 5)/(x2 – 3x + 2) = 6/x
⇒ 3x2 – 5x = 6x2 – 18x + 12 [On cross multiplying]
⇒ 3x2 – 13x + 12 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – (9 + 4)x + 12 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 9x – 4x + 12 = 0
⇒ 3x(x – 3) – 4(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (3x – 4)(x – 3) = 0
⇒ 3x – 4 = 0 or x – 3 = 0
⇒ x = 4/3 or x = 3
64. 1/(x + 1) + 2/(x + 2) = 5/(x + 4), x ≠ -1, -2, -4
Solution
1/(x + 1) + 2/(x + 2) = 5/(x + 4), x ≠ -1, -2, -4
⇒ (x + 2 + 2x + 2)/(x + 1)(x + 2) = 5/(x + 4)
⇒ (3x + 4)/(x2 + 3x + 2) = 5/(x + 4)
⇒ (3x + 4)(x + 4) = 5(x2 + 3x + 2)
⇒ 3x2 + 16x + 16 = 5x2 + 15x + 10
⇒ 2x2 – x – 6 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 4x + 3x – 6 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 2) + 3(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 2)(2x + 3) = 0
⇒ 3x2 + 16x + 16 = 5x2 + 15x + 10
⇒ 2x2 – x – 6 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 4x + 3x – 6 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 2) + 3(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 2)(2x + 3) = 0
⇒ x – 2 = 0 or 2x + 3 = 0
⇒ x = 2 or x = -3/2
Hence, 2 and -3/2 are the roots of the given equation.
65. 3(3x – 1)/(2x + 3) – 2(2x + 3)/(3x – 1) = 5, x ≠ 1/3, -3/2
Solution
3(3x – 1)/(2x + 3) – 2(2x + 3)/(3x – 1) = 5, x ≠ 1/3, -3/2
⇒ 3(3x – 1)2 – 2(2x + 3)2/(2x + 3)(3x – 1) = 5
⇒ 3(9x2 – 6x + 1) – 2(4x2 + 12x + 9)/(6x2 + 7x – 3) = 5
⇒ (27x2 – 18x + 3 – 8x2 – 24x – 18)/(6x2 + 7x – 3) = 5
⇒ (19x2 – 42x – 15)/(6x2 + 7x – 3) = 5
⇒ 19x2 – 42x – 15 = 30x2 + 35x – 15
⇒ 11x2 + 77x = 0
⇒ 11x(x + 7) = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x + 7 = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x = - 7
Hence, 0 and -7 are the roots of the given equation.
66. 3(7x + 1)/(5x – 3) – 4(5x – 3)/(7x + 1) = 11, x ≠ 3/5, - 1/7
Solution
3(7x + 1)/(5x – 3) – 4(5x – 3)/(7x + 1) = 11, x ≠ 3/5, - 1/7
⇒ {3(7x + 1)2 – 4(5x – 3)2}/(5x – 3)(7x + 1) = 11
⇒ 3(49x2 +1 4x + 1) – 4(25x3 – 30x + 9)/(35x2 – 16x – 3) = 11
⇒ (147x2 + 42x + 3 – 100x2 + 120x – 36)/(35x2 – 16x – 3) = 11
⇒ (47x2 + 162x – 33)/(35x2 – 16x – 3) = 11
⇒ 338x(x – 1) = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = 0 x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x = 1
Hence, 0 and 1 are the roots of the given equation.
67. (4x – 3)/(2x + 1) – 10(2x + 1)/(4x – 3) = 3, x ≠ -1/2, 3/4
Solution
Given:
(4x – 3)/(2x – 1) – 10(2x + 1)/(4x – 3) = 3
Putting (4x – 3)/(2x + 1) = y, we get:
y - 10/y = 3
⇒ (y2 – 10)/y = 3
⇒ y2 – 10 = 3y [On cross multiplying]
⇒ y2 – 3y – 10 = 0
⇒ y2 – (5 – 2)y – 10 = 0
⇒ y2 – 5y + 2y – 10 = 0
⇒ y(y – 5) + 2(y – 5) = 0
⇒ (y – 5)(y + 2) = 0
⇒ y – 5 = 0 or y + 2 = 0
⇒ y = 5 or y = -2
Case I:
If y = 5, we get:
⇒ (4x – 3)/(2x + 1) = 5
⇒ 4x – 3 = 5(2x + 1) [On cross multiplying]
⇒ 4x – 3 = 10x + 5
⇒ -6x = 8
⇒ -6x = 8
⇒ x = 8/6
⇒ x = -(4/3)
Case II:
If y = -2, we get:
(4x – 3)/(2x + 1) = -2
⇒ 4x – 3 = -2(2x + 1)
⇒ 4x – 3 = -4x – 2
⇒ 8x = 1
⇒ x = 1/8
Hence, the roots of the equation are –(4/3) and 1/8.
68. (x/(x + 1))2 – 5(x/(x + 1)) + 6 = 0, x ≠ b, a
Solution
(x/(x + 1))2 – 5(x/(x + 1)) + 6 = 0
Putting x/(x + 1) = y, we get:
y2 – 5y + 6 = 0
⇒ y2 – 5y + 6 = 0
⇒ y2 – (3 + 2) y + 6 = 0
⇒ y2 – 3y – 2y + 6 = 0
⇒ y(y – 3) – 2(y – 3) = 0
⇒ (y – 3)(y – 2) = 0
⇒ y – 3 = 0 or y – 2 = 0
⇒ y = 3 or y = 2
Case I:
If y = 3, we get
x/(x + 1) = 3
⇒ x = 3(x + 1) [On cross multiplying]
⇒ x = 3x + 3
⇒ x = -3/2
Case II:
If y = 2, we get:
x(x + 1) = 2
⇒ x = 2(x + 1)
⇒ x = 2x + 2
⇒ - x = 2
⇒ x = -2
Hence, the roots of the equation are -3/2 and -2.
69. a/(x – b) + b(x – a) = 2, x ≠ b, a
Solution
a/(x – b) + b/(x – a) = 2
⇒ a – x + b = 0 or 2x – (a + b) = 0
⇒ x = a + b or x = (a + b)/2
Hence, the roots of the equation are (a + b) and (a + b)/2.
70. a/(ax – 1) + b/(bx – 1) = (a + b), x ≠ 1/a, 1/b
Solution
a/(ax – 1) + b/(bx – 1) = (a + b)
⇒ [a/(ax – 1) – b] + [b/(bx – 1) – a] = 0
⇒ [a – b(ax – 1)/(ax – 1)] + [b – a(bx – 1)/(bx – 1)] = 0
⇒ (a – abx + b)/(ax – 1) + (a – abx + b)/(bx – 1) = 0
⇒ (a – abx + b)[1/(ax – 1) + 1/(bx – 1)] = 0
⇒ (a – abx + b)[(bx – 1) + (ax – 1)/(ax – 1)(bx – 1)] = 0
⇒ (a – abx + b)[(a + b)x – 2/(ax – 1)(bx – 1)] = 0
⇒ (a – abx + b)[(a + b)x – 2] = 0
⇒ a – abx + b = 0 or (a + b)x – 2 = 0
⇒ x = (a + b)/ab or x = 2/(a + b)
Hence, the roots of the equation are (a + b)/ab and 2/(a + b).
71. 3(x + 2) + 3-x = 10
Solution
3(x + 2) + 3-x = 10
3x.9 + 1/3x = 10
Let 3x be equal to y.
∴ 9y + 1/y = 10
⇒ 9y2 + 1 = 10y
⇒ 9y2 – 10y + 1 = 0
⇒ (y – 1)(9y – 1) = 0
⇒ y – 1 = 0 or 9y – 1 = 0
⇒ y = 1 or y = 1/9
⇒ 3xx = 1 or 3x = 1/9
⇒ 3x = 30 or 3x = 3-2
⇒ x = 0 or x = -2
Hence, 0 and -2 are the roots of the given equation.
72. 4(x +1) + 4(1 – x) = 10
Solution
Given:
4(x + 1) + 4(1 – x) = 10
⇒ 4x .4 + 41.1/44 = 10
Let 4x be y.
∴ 4y + 4/y = 10
⇒ 4y2 – 10y + 4 = 0
⇒ 4y2 – 8y – 2y + 4 = 0
⇒ 4y(y – 2) – 2(y – 2) = 0
⇒ y = 2 or y = 2/4 = 1/2
⇒ 4x = 2 or 1/2
⇒ 4x = 22x or 21 or 22x = 2-1
⇒ x = ½ or x = -1/2
Hence, 1/2 and -1/2 are roots of the given equation.
73. 22x – 3.2(x + 2) + 32 = 0
Solution
22x – 3.2(x + 2) + 32 = 0
⇒ (2x)2 – 3.2x.22 + 32 = 0
Let 2x be y.
∴ y2 – 12y + 32 = 0
⇒ y2 – 8y – 4y + 32 = 0
⇒ y(y – 8) – 4(y – 8) = 0
⇒ (y – 8) = 0 or (y – 4) = 0
⇒ y = 8 or y = 4
∴ 2x = 8 or 2x = 4
⇒ 2x = 23 or 2x = 22
⇒ x – 2 or 3
Hence, 2 and 3 are the roots of the given equation.