NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds (MCQ, SAQ and LAQ)
Chapter Name | NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Ch 4 Carbon and its Compounds |
Topics Covered |
|
Related Study |
|
Objective Type Questions for Carbon and its Compounds
1. Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of
(a) carbon monoxide only
(b) carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
(c) carbon dioxide only
(d) coal
Solution
(c) carbon dioxide only
2. Which of the following statements are usually correct for carbon compounds? These
(i) are good conductors of electricity
(ii) are poor conductors of electricity
(iii) have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(iv) do not have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Solution
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Carbon compounds form covalent bonds hence they have very weak force of attraction. Carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity.
3. A molecule of ammonia (NH3) has
(a) only single bonds
(b) only double bonds
(c) only triple bonds
(d) two double bonds and one single bond
Solution
(a) only single bonds
Nitrogen has 3 electron in its outermost shell and hydrogen has 1. 3 hydrogen atoms combine with 1 nitrogen atom to make ammonia. These bonds are single bonds.
4. Buckminsterfullerene is an allotropic form of
(a) phosphorus
(b) sulphur
(c) carbon
(d) tin
Solution
(c) carbon
Diamond, Graphite, Lonsdaleite, C60 (Buckminsterfullerene or buckyball), C40, C70, Amorphous carbomn, single-walled carbon nanotube, or buckytube are the allotropes of Carbon.
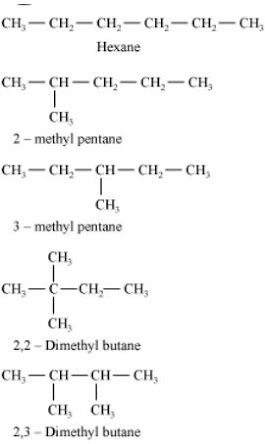
5. Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane ?
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Solution
(c) (i) and (ii)
Chemical formula of Butane isC4H10 , here option iii) and iv) have 8 hydrogen atoms, hence they are wrong.
In the above given reaction, alkaline KMnO4 acts as
(a) reducing agent
(b) oxidising agent
(c) catalyst
(d) dehydrating agent
Solution
(b) oxidising agent
Two Hydrogen atoms are replaced by an atom of oxygen making oxidation of ethanol. Here addition of oxygen is provided by potassium.
7. Oils on treating with hydrogen in the presence of palladium or nickel catalyst form fats. This is an
example of
(a) Addition reaction
(b) Substitution reaction
(c) Displacement reaction
(d) Oxidation reaction
Solution
(a) Addition reaction
Here, Hydrogen is added to oil, hence it is an addition reaction.
8. In which of the following compounds, — OH is the functional group?
(a) Butanone
(b) Butanol
(c) Butanoic acid
(d) Butanal
Solution
(b) Butanol
Compound with OH Functional group will have a suffix -ol in them. Hence, answer is (b) Butanol.
9. The soap molecule has a
(a) hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
(b) hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
(c) hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
(d) hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
Solution
(a) hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
Because of hydrophobic tail Oil and grease is trapped inside a micelle. Hydrophobic head makes the outer surface of micelle. Hence micelle is easily washed by water.
10. Which of the following is the correct representation of electron dot structure of nitrogen ?
Solution
(d)
In this structure Nitrogen atoms gets 8 electron whereas in other options it is different.
11. Structural formula of ethyne is
(a) H - C ☰ C - H
(b) H3 - C ☰ C - H
Solution
(a)
Chemical formula of Ethyne is C2H2 , Hence answer is (a).
12. Identify the
unsaturated
compounds from the following
(i) Propane
(ii) Propene
(iii) Propyne
(iv) Chloropropane
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Solution
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Propene has double bond and Propyne is having triple bond. Hence they are unsaturated compounds.
13. Chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbons at room temperature in the
(a) absence of sunlight
(b) presence of sunlight
(c) presence of water
(d) presence of hydrochloric acid
Solution
(b) presence of sunlight
In presence of sunlight Chlorine reacts with Hydrocarbons and displaces Hydrogen atoms.
14. In the soap micelles
(a) the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the
cluster.
(b) ionic end of soap is in the interior of the cluster and the carbon chain is out of the cluster.
(c) both ionic end and carbon chain are in the interior of the cluster
(d) both ionic end and carbon chain are on the exterior of the cluster
Solution
(a) the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
A micelle is a spherical aggregate soap molecules in soap solution. In the soap micelles the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.(a) 5 covalent bonds
(b) 12 covalent bonds
(c) 16 covalent bonds
(d) 17 covalent bonds
Solution
(c) 16 covalent bonds
16. Structural formula of benzene is
Solution
(c)
Chemical formula of Benzene is C6H6. In option call the arms of carbon atoms are occupied hence it is the right answer.
17. Ethanol reacts with sodium and forms two products. These are
(a) sodium ethanoate and hydrogen
(b) sodium ethanoate and oxygen
(c) sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
(d) sodium ethoxide and oxygen
(c) sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
2Na + 2CH3CH2OH → 2CH3CH2ONa + H2
(d)
(a) 50% – 60% acetic acid in alcohol
(b) 5% – 8% acetic acid in alcohol
(c) 5% – 8% acetic acid in water
(d) 50% – 60% acetic acid in water
(c) 5% – 8% acetic acid in water
(i) mineral acids are completely ionised
(ii) carboxylic acids are completely ionised
(iii) mineral acids are partially ionised
(iv) carboxylic acids are partially ionised
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
(a) (i) and (iv)
(a) helium
(b) neon
(c) argon
(d) krypton
(b) neon
(c)
(d)
(ii) H3C – C ≡ C – CH3
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(a) CH4
(b) C2H6
(c) C3H8
(d) C4H8
(a) Propanal
(b) Propanone
(c) Ethanol
(d) Ethanal
(a) Propanal
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine
(d) (i) and (iv)
(a) ethyne
(b) ethene
(c) propyne
(d) methane
(b) ethene
Short Answer Questions for Carbon and its Compounds
(a) Pentanoic acid
(a) Alcohol
Detergents are better than soaps because detergents are ammonium or sulphonate salts of long chain carboxylic acids. Charged ends of theses will not for precipitate with calcium and magnesium present in hard water. On the other hand soaps will form precipitate with calcium and magnesium ions present in the hard water.
(a) CH3 CO CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
(b) CH3 CH2 CH2 COOH
(c) CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CHO
(d) CH3 CH2 OH
Solution
(a) Ketone
(b) Carboxylic acid
(c) Aldehyde
(d) Alcohol
36. How is ethene prepared from ethanol? Give the reaction involved in it.
Solution
Ethanol is heated at 443 K along with excess Sulphuric acid to obtain Ethene.
2CH3–CH2–OH + 2Na → 2CH3–CH2–ONa + H2
(a) CCl4 - Carbon Tetra chloride
(b) Carbon dioxide – CO2
41. In electron dot structure, the valence shell electrons are represented by crosses or dots.
(a) The atomic number of chlorine is 17. Write its electronic configuration
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of chlorine molecule
Catenation is shown by both Silicon and Carbon. Silicon bonds are less stable and reactive whereas bonds formed by Carbon bonds are very strong hence carbon shows better catenation than Silicon.
Saturated Hydrocarbons burns with clean flame and produce no soot where as non-saturated Hydrocarbons burns with yellow flame and produces lot of soot. Ethane is saturated hydrocarbon and it burns with clean flame with no soot. Ethene is unsaturated hence it burns with yellow flame producing lot of soot.
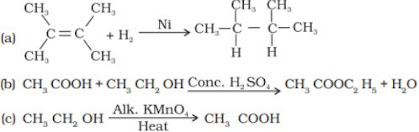
46. What is the role of metal or reagents written on arrows in the given chemical reactions ?
Long Answer Questions for Carbon and its Compounds
When ethanoic acid reacts with Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate with production of Sodium Ethanoate and producing Carbon dioxide gas.
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Here, salt X is sodium Ethanoate and gas evolved is Carbon dioxide.
Activity
- Set up the experiment as shown in figure.
- Take a spoon full of Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate in a test-tube and add 2ml of dilute ethanoic acid.
- Brisk effervescence occur in test tube.
- Pass the produce gas into lime water
- Lime water turn milky confirming the evolution of CO2 .
(b) Give the structural differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each.
(c) What is a functional group? Give examples of four different functional groups.
Example: Ethane, Methane
- Saturated Hydrocarbon: Ethane, Methane
- Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Ethyne, Ethene
Example: CHO-Aldehyde, OH-Hydroxyl , COOH- Carboxylic acid.
(b) What is saponification? Write the reaction involved in this process.
(a) Carbon tetra chloride - CCl4 .
CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3COONa + C2H5OH
(I) Compound C is Ethanoic acid [Acetic acid]
It reacts with sodium metal to form a compound called R. R is Sodium Ethanoate.
2CH3COOH + 2Na → 2CH3COONa + H2
So compound S is Ester of Ethyl ethanoate and compound A is Ethanol
(III) CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3COONa + C2H5OH.
- Compound R is again Sodium Ethanoate.
- Compound C is Ethanoic acid
- A is Ethanol
- S is Ester R is sodium Ethanoate.
(a) What change would you observe in the calcium hydroxide solution taken in tube B?
(b) Write the reaction involved in test tubes A and B respectively.
(c) If ethanol is given instead of ethanoic acid, would you expect the same change?
(d) How can a solution of lime water be prepared in the laboratory?
(a) Calcium hydroxide solution would become milky
(b) Reaction in Tube A
CH3COOH + NAHCO3 → CH3COONA + CO2 + H2O
Reaction in tube B
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(a) ethanol to ethene.
(b) propanol to propanoic acid. Write the reactions.
(a) Ethene is formed when ethanol is heated at 443 K with excess of concentrated sulphuric acid.
(b) Propanol is treated with alkaline Potassium permanganate or acidified Potassium - di - chromate to obtain propanoic acid.
(a) Hydrogenation reaction
(b) Oxidation reaction
(c) Substitution reaction
(d) Saponification reaction
(e) Combustion reaction
(a) Addition of hydrogen to unsaturated Hydrocarbons to convert into saturated hydrocarbons is called as Hydrogenation. This process is used in the conversion of unsaturated vegetable oil into saturated fats.
Example:
(e) Combustion is the burning of a substance in presence of Oxygen.
Example: CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat and light
Compound A is Ethanol
Compound A = CH3CH2OH
Compound B is Ethane
Compound B = CH2 = CH2
Compound C = CH3 - CH3