Frank Solutions for Chapter 6B Light- Reflection and Refraction Class 9 Physics ICSE
1. Name the mirror having a wider field of view.
Answer
Convex mirror has a wider field of view.
2. Name the mirror which always produces an erect image of the objects.
Answer
Convex mirror always produces an erect image of the object.
3. What kind of mirror is used in vehicles to see the traffic on the rear side?
Answer
Convex mirror is used in vehicles to see the traffic on rear side.
4. If you want to see an enlarged image of your face, state whether you will use a convex mirror or a concave mirror?
Answer
We will use convex mirror to see an enlarged image of our face.
5. An object is placed at a long distance in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm. State the position of the image.
Answer
Image of object placed at a long distance in front of a convex mirror is formed at principal focus. Radius of curvature of convex mirror is 20 cm.
Focal length of convex mirror = radius of curvature/2.
Focal length of convex mirror = 20/2 = 10 cm.
So image will form at principal focus 10 cm away from pole.
6. Name the spherical mirror which can produce a real and diminished image of an object.
Answer
Concave mirror can produce real and diminished image of the object.
7. What do you mean by focal length of a mirror?
Answer
The distance of the principal focus from the pole of the mirror is called the focal length of the mirror.
8. Name the type of mirror having a focal length of +20 cm.
Answer
The mirror having +20 cm as its focal length is a convex mirror because focal length is taken positive only in case of convex mirror.
9. What is the focal length of a plane mirror?
Answer
The focal length of plane mirror is infinity.
10. Name the type of mirror having a focal length of -15 cm.
Answer
The mirror having -15 cm as its focal length is a concave mirror because focal length is taken negative only in case of concave mirror.
11. What do you mean by principle axis?
Answer
Principal axis is the straight line passing through the pole and the centre of curvature.
12. Define linear magnification of a mirror.
Answer
Linear magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object. It is taken to be positive for an image to be virtual and erect and negative when image is real and inverted.
Magnification = height of image/height of object.
13. Define pole of a mirror.
Answer
Pole is the centre of the reflecting surface, in this case spherical mirror.
14. What do you mean by centre of curvature of a mirror?
Answer
Centre of curvature is the centre of the imaginary sphere to which the mirror belongs.
15. State three characteristics of light.
Answer
Three characteristics of light are:-
- Light waves can travel through vacuum.
- Light waves are transverse waves.
- The velocity of light in vacuum is 3×108 m/s.
16. Give three differences between sound and light.
Answer
Three distinctions between light and sound waves are
- Light waves can travel through vacuum while sound waves cannot.
- Light waves are transverse waves while sound waves are longitudinal waves.
- The velocity of light in air is 3×108 m/s while the speed of light in air is just about 330 m/s.
17. State three characteristics of the image formed by a concave mirror.
Answer
- When position of object is at infinity, concave mirror forms a point and Real image at Focus point.
- When position of object is beyond C, concave mirror forms a Diminished, Real and inverted image between F and C.
- When position of object is at C, concave mirror forms a Magnified, Real and inverted image at C.
18. State three characteristics of the image formed by a convex mirror.
Answer
Image formed by a convex mirror is always Diminished, Virtual and Erect.
19. Give three uses of concave mirrors.
Answer
Concave mirrors are used in reflecting microscope, in shaving and make up glasses and in ophthalmoscope.
20. Write the sign convection used in optics.
Answer
- The distance from the pole in the direction of incident ray is taken positive.
- The distance from the pole in the direction opposite to the incident ray is taken negative.
21. What is a mirror formula? Define linear magnification produced by a mirror?
Answer
Mirror formula is the relation between the focal length f of the mirror, the distance u of the object from the pole of the mirror, and the distance v of the image from the pole.
Mirror formula is 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
Linear magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object. It is taken to be positive for an image to be virtual and erect and negative when image is real and inverted.
Magnification = height of image/height of object.
22. Define linear magnification. Does it have any units? Write down a formula for the magnification produced by a concave mirror in terms of image distance and object distance.
Answer
Linear magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object. It is taken to be positive for an image to be virtual and erect and negative when image is real and inverted.
Magnification produced by concave mirror is:
Magnification = height of image/height of object.
It is a pure ratio and does not have any units.
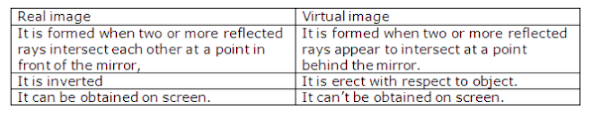
23. Distinguish between real and virtual images.
Answer
Differences between real and virtual images
24. Distinguish between regular and irregular reflection.
Answer
A smooth and polished surface causes regular reflection while a rough and unpolished surface causes irregular reflection.
25. What do you mean by reflection? State the laws of reflection.
Answer
When rays of light fall on a surface, they are turned back into the same medium in accordance with some definite laws. This process is known as reflection.
Reflection obeys following two laws
- The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
- The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always equal.
26. How will you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror without touching them?
Answer
You can distinguish between plane mirror, a concave mirror, and a convex mirror without touching them. When you look into these mirrors by bringing your face close to each mirror, they will produce an image of your face of different types.
- A plane mirror will produce an image of the same size as your face.
- A concave mirror will produce a magnified image of your face.
- A convex mirror will produce Diminished image of your face.
27. How can you distinguish between a convex mirror and concave mirror? Explain.
Answer
You can distinguish between a concave mirror and a convex mirror without touching them. When you look into these mirrors by bringing your face close to each mirror, they will produce an image of your face of different types.
- A concave mirror will produce a magnified image of your face.
- A convex mirror will produce Diminished image of your face.
28. The boxes in fig. 1 (a, b, ¢) represent mirrors; insert a mirror which will reflect the incident ray as shown in the diagram.
Answer(i) Plane mirror
(ii) Convex Mirror
(iii) Concave Mirror
29. Give two uses of convex mirror.
Answer
Uses of concave mirror:
- Concave mirrors are used in reflecting microscope
- Concave mirrors are used in shaving and make up glasses.
Uses of convex mirror: Convex mirrors are used as a rear view mirror in automobiles as it provides a wider view of following traffic.
30. You can see the reflection of your clearly on a polished table-top is not polished. Explain.
Answer
We can see the reflection of our face on a polished table top because a regular reflection occurs in case of a polished surface while on a unpolished table top irregular reflection occurs which make image of our face unclear.
31. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, correct them.
(i) The angle of incidence is the angle made by the incident ray with the plane mirror.
(ii) If a ray of light incident on a plane mirror is such that it makes an angle of 30° with the mirror, then the angle of reflection is 60°.
(iii) If the incident ray makes an angle of X° with the normal, then the reflected ray ts 2X9.
(iv) The image in a plane mirror is situated in the mirror.
(v) The image formed in a plane mirror is real, erect and same size as that of the object.
Answer
(i) The angle of incidence is the angle made by the incident ray with the plane mirror. (FALSE)
Correct statement is the angle of incidence is the angle made by the incident ray with the normal to the surface of plane mirror.
(ii) If a ray of light incident on a plane mirror is such that it makes an angle of 30° with the normal, then the angle of reflection is 60° (FALSE)
Correct statement is if a ray of light incident on a plane mirror is such that it makes an angle of 30° with the normal, then the angle of reflection is 30°.
(iii) If the incident ray makes an angle of Xo with the normal, then the angle between the incident ray and reflected ray is 2X°. (TRUE)
(iv) The image formed in a plane mirror is real, erect and same size as that of the object. (FALSE)
Correct statement is the image formed in a plane mirror is virtual, erect and same size as that of the object.
32. When a ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of 15° with the mirror, what will be the angle through which the ray will be deviated ? Illustrate with a ray diagram (Fig. 2).
AnswerReflection obeys following two laws
(a) The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(b) The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always equal. According to these two laws this ray will deviate like this:
33. You are provided with two plane mirrors. Draw a ray diagram to show how the ray of light can be turned through an angle of 180°.
Answer
Two planes when put in this way then they will turn the incident ray by 180°.
34. What are the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror?
Answer
The image formed by a plane mirror is erect and virtual. It is a laterally inverted image. The image formed is of the same size as that of the object. Also, the image and the object are equidistant from the mirror.
35. The word PLATE written on a paper is held in front of a plane mirror.
Write down the letters as seen in each of the following cases [Fig. 3(a)] and
(b)
(i) The paper is held parallel to the mirror.
(ii) The paper is held perpendicular to the mirror.
Answer(i) When the paper is held parallel to the mirror.
(ii) When paper is held perpendicular to the mirror.
36. A boy is standing in front of a plane mirror at a distance of 3 m from it.
(i) What is the distance between the boy and his image?
(ii) If the boy moves 1 m backward, find the distance between the image and the boy.
Answer
Given, distance of boy from the mirror = 3m
(a) Distance of image from mirror = distance of boy from the mirror = 3m
Distance between boy and his image = distance of boy from the mirror + distance of image from mirror
= 3 + 3
= 6 m
(b) Now, distance of boy from the mirror = 4m
Distance of image from mirror = 4m
Distance between boy and his image = distance of boy from the mirror + distance of image from mirror
= 4 + 4
= 8m.
37. Draw a neat and labeled ray diagram of a simple periscope. Give two uses of a periscope.
Answer
Periscope is used to see over the top of an obstacle. It is also used in submarines for observing for movement of ships. It can be used from the trenches for observing the movement on the surface of earth.
38. Complete the ray diagram to show the image observed by the eye after reflection [Fig. 4 (a)), (b)]
AnswerThe image observed by the eye after reflection from a plane mirror can be completed as follows:
(a)
(b)
39. Define the following terms:
(i) Pole
(ii) Centre of curvature
(iii) Principle focus
(iv) Principle axis
(v) Focus of a concave mirror
(vi) Normal
Answer
(a) Pole is the centre of the reflecting surface, in this case spherical mirror.
(b) Centre of curvature is the centre of the imaginary sphere to which the mirror belongs
(c) Principal focus of a spherical mirror is a point on the principal axis of the mirror, where all the rays travelling parallel to the principal axis and close to it after reflection from the mirror, converge to or appear to diverge from.
(d) Principal axis is the straight line passing through the pole and the centre of curvature.
(e) Focus of a concave mirror is a point on the principal axis of the mirror, where all the rays travelling parallel to the principal axis and close to it after reflection from the mirror converge to that point.
(f) Normal to the surface of a mirror at any point is the straight line at right angle to the tangent drawn at that point.
40. Locate the images formed when the object is placed between two plane as shown in fig. 5 (a) and (b).
(a)
(b)(a) When two mirrors are held perpendicular then number of images is 3 according to rule
Number of images = 360/x - 1 if 360/x is even
Number of images is 360/90 - 1 = 41 = 3 images.
(b) When two mirrors are held parallel to each other then, infinite numbers of image are formed and first two images are shown in this figure.
41. Complete the path of incident ray in each of the following cases (Fig 6).
AnswerComplete path of the incident ray in following cases are:
(i)
42. By geometrical construction, find the position of the image in fig. 7.
AnswerPosition of image is exactly below the position of object as in the figure.
43. An object is placed in front of a convex mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale drawing show the formation of image and state the nature of image.
Answer
Image formed is virtual, Diminished and erect.44. (a) Draw a ray diagram to show that a convex mirror has a wider field of view.
(b) A concave mirror can be used to produce a parallel beam of light. Draw a ray to illustrate this.
Answer
(a) In case of convex mirror all rays incident parallel to principal axis appear to diverge from a Focal point. So it has a wider field of view as it converge all rays to a single point.
(b) In case of concave mirror if object is placed at Focal point then ray emerging from it after reflecting from mirror would be parallel to principal axis.
45. An object 10 cm high is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a spherical mirror of focal length 25 cm. By scale drawing find the nature, position and magnification of image in each of the following cases:
(a) Concave mirror,
(b) Convex mirror.
Answer
(a) Focal length = 25 cm.
Object distance = 20 cm.
Height of object = 10cm
Image is virtual, erect and magnified.
(b) Focal length = 25 cm.
Object distance = 20 cm.
Height of object = 10 cm.
Image is virtual, erect and diminshed.
46. An object is placed in front of a concave mirror as shown in fig.8. By scale drawing, find the nature of image. Given f = 10 cm, v = 30cm.
AnswerFocal length of concave mirror = 10 cm.
Object distance = 30 cm
Image is real, inverted and diminished.
47. An object 5 cm in height is placed at a distance of 30 m in front of a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm. By scale drawing find the nature, size, position and magnification of the image.
Answer
Height of object = 5 cm.
Distance of object = 30 cm.
Focal length of mirror = 40 cm.
Image is real, inverted and diminished.
48. Fig. 9 shows a concave mirror MM’ on which a ray of light incident from a Point P gets reflected to meet the principle axis at O.
(a) Find, by construction, the position of the centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
(b) Write down the value for the radius of curvature of the mirror.
(c) Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
(d) Which relation is used in deducing the focal length from the radius of curvature?
Answer
(a) Centre of curvature can be determined by constructing the imaginary sphere to which lens belongs.
(b) Value of radius of curvature can be found by measuring the radius of this imaginary sphere geometrically.
(c) Focal length is the midpoint of pole and centre of curvature.
(d) focal length of mirror = centre of curvature/2.
Centre of curvature = 2.8 cm.
Focal length of mirror = 1.4.cm.
Focal length = radius of curvature/2.
49. The diagram below shows the parallel rays incident on a convex mirror. C is the centre of curvature of mirror. By drawing the paths of the reflected rays, label the focus F and hence find the focal length of the mirror.
AnswerWe know when incident ray is parallel to principal axis then they appear to diverge from a point F.Geometrically we can find this value and this comes to 2 cm.
Centre of curvature = 4 cm.
Focal length = centre of curvature/2