Exercises
1. Write in detail the structure of a typical flower studied by you with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer
Answer
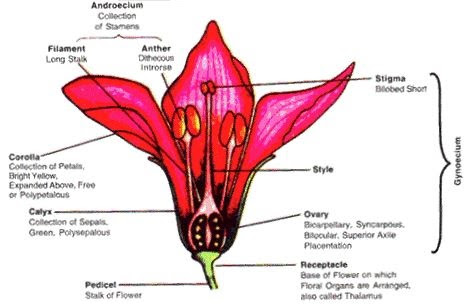
A flower is the reproductive unit in angiosperms. It is a modified shoot in which internodes are shortened and leaves are modified into floral structure. Flower is meant for sexual reproduction.
A typical flower has four different kinds of whorls arranged successively on the swollen parts of a flower stalk. Flower stalk consists of the stalk called pedicel and the swollen upper part called thalamus bearing the floral leaves.
The different floral whorls are calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium. Calyx and corolla are accessory whorls, while androecium and gynoecium are reproductive whorls.
Calyx – The calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower and its members are called sepals. Generally, sepals are green, leaf like and protect the inner whorls of the flower in bud stage. They are also involved in producing food by photosynthesis. The calyx may be gamosepalous (sepals united) or polysepalous (sepals free).
Corolla – It is the second whorl composed of floral leaves called petals. Petals are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination. Petals also protect the inner whorls. Like calyx, corolla may be also free (gamopetalous) or united (polypetalous).
The shape and colour of corolla vary greatly in plants.
Androecium – It is the third whorl and is the male reproductive whorl of a flower.
Androecium is composed of one or more stamens. Each stamen consists of three parts:
Ovary is the swollen basal part containing ovules. Each ovary bears one or more ovules attached to a flattened, cushion-like structure called placenta.
Style is the elongated thread like structure attached to the apex of the ovary. It connects the ovary to the stigma.
The stigma is situated at the tip of the style and is the receptive surface for pollen grains.
The different floral whorls are calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium. Calyx and corolla are accessory whorls, while androecium and gynoecium are reproductive whorls.
Calyx – The calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower and its members are called sepals. Generally, sepals are green, leaf like and protect the inner whorls of the flower in bud stage. They are also involved in producing food by photosynthesis. The calyx may be gamosepalous (sepals united) or polysepalous (sepals free).
Corolla – It is the second whorl composed of floral leaves called petals. Petals are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination. Petals also protect the inner whorls. Like calyx, corolla may be also free (gamopetalous) or united (polypetalous).
The shape and colour of corolla vary greatly in plants.
Androecium – It is the third whorl and is the male reproductive whorl of a flower.
Androecium is composed of one or more stamens. Each stamen consists of three parts:
- Filament – It is the lower stalk of the stamen.
- Anther – Filament bears a bilobed fertile structure called anther at its distal end.
Each lobe contains two pollen sacs. The pollen grains are produced in pollen-sacs. - (iii) Connective – Filament of the stamen is extended in between the two anther lobes called connective.
Ovary is the swollen basal part containing ovules. Each ovary bears one or more ovules attached to a flattened, cushion-like structure called placenta.
Style is the elongated thread like structure attached to the apex of the ovary. It connects the ovary to the stigma.
The stigma is situated at the tip of the style and is the receptive surface for pollen grains.
2. Define the following terms and mention their main functions:
(a) Inflorescence
(b) Gynoecium
(c) Placentation
(d) Incomplete flower
(e) Perianth
Answer
(a) Inflorescence
(b) Gynoecium
(c) Placentation
(d) Incomplete flower
(e) Perianth
Answer
(a) Inflorescence – The arrangement of flowers on the floral axis is called inflorescence.
Function: Inflorescence facilitates the best arrangement and display of flowers on a branch without any sort of overcrowding. It also facilitates pollination via a prominent visual display and more efficient pollen uptake and deposition.
(b) Gynoecium – It is the innermost whorl of the flower bearing the female reproductive parts.
Function: The ovary of gynoecium produces ovules which bear the female gamete.
(c) Placentation – The manner in which placenta and ovules are arranged inside the ovary wall is known as placentation.
Function: Placentation helps in the best arrangement of ovules within the ovary.
Placentation also helps in plant classification.
(d) Incomplete flower – A flower lacking one whorl out of the four whorls is said to be incomplete flower.
Function: An incomplete flower contains either male or female reproductive organs.
(e) Perianth – When the calyx and corolla are not distinct in a flower (eg. lily), the whorl is collectively called perianth.
Function: The members of perianth, called petals are usually brightly coloured and bear scent. This attracts insects which aids in pollination. They also protect the flower in bud condition.
Function: Inflorescence facilitates the best arrangement and display of flowers on a branch without any sort of overcrowding. It also facilitates pollination via a prominent visual display and more efficient pollen uptake and deposition.
(b) Gynoecium – It is the innermost whorl of the flower bearing the female reproductive parts.
Function: The ovary of gynoecium produces ovules which bear the female gamete.
(c) Placentation – The manner in which placenta and ovules are arranged inside the ovary wall is known as placentation.
Function: Placentation helps in the best arrangement of ovules within the ovary.
Placentation also helps in plant classification.
(d) Incomplete flower – A flower lacking one whorl out of the four whorls is said to be incomplete flower.
Function: An incomplete flower contains either male or female reproductive organs.
(e) Perianth – When the calyx and corolla are not distinct in a flower (eg. lily), the whorl is collectively called perianth.
Function: The members of perianth, called petals are usually brightly coloured and bear scent. This attracts insects which aids in pollination. They also protect the flower in bud condition.
3. Write down the different positions of floral leaves on the thalamus in detail?
Answer
Based on the position of calyx, corolla and androecium in respect to the ovary on thalamus, There are three floral whorl conditions. These are:
- Hypogyny - In this flower, the ovary occupies the highest position on the thalmus, while the petals, sepals and stamens are separately inserted below the ovary. the ovary in such flowers is said to be superior. E.g., Mustard and china rose.
- Perigyny - In this condition, the margin of the thalamus grows upwards to from a cup-shaped structure called calyx tube enclosing the ovary. the ovary here is said to be half inferior. E.g., plum and rose
- Epigyny - In this flower, the margin of thalamus grows upwards enclosing the ovary completely and getting fused with it. the other part of the flower are above the ovary. Hence, the ovary is said to be inferior. E.g. Sunflower, flowers of cucumber
4. What is the significance of flowers in the plant and how many types of flowers are there?
Answer
Answer
The flower is the reproductive unit in the angiosperms and is meant for sexual reproduction. Flowers produce seeds from which new plants grow in future. So the main function of flower is to perpetuate the species.
There are six different types of flowers. These are complete, incomplete, bisexual, unisexual, actinomorphic and zygomorphic.
5. Write a difference between
(a) Calyx and Corolla
(b) Inflorescence and Flower
(c) Androecium and Gynoecium
(d) Hypogyny and Perigyny
(e) A complete flower and an Incomplete Flower
(a) Calyx and Corolla
(b) Inflorescence and Flower
(c) Androecium and Gynoecium
(d) Hypogyny and Perigyny
(e) A complete flower and an Incomplete Flower
Answer
(a) Difference between Calyx and Corolla
| Calyx | Corolla |
| It is the outermost whorl of flower. | It is the second whorl of flower. |
| Its members are called sepals | Its members are called petals. |
| Sepals of calyx protect the inner whorls of the flower in bud stage. | Petals are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination; they also protect the inner whorls. |
(b) Difference between Inflorescence and Flower
| Inflorescence | Flower |
| It refers to the arrangement of flowers on the floral axis. | Flower is a modified shoot in which internodes are shortened and leaves are modified into floral structure. |
| Inflorescence is of two types - Racemose and cymose | Flowers are of six types - complete, incomplete, bisexual, unisexual, actinomorphic and zygomorphic. |
(c) Difference between Androecium and Gynoecium
| Androecium | Gynoecium |
| It is the third whorl of a flower | It is the innermost whorl of a flower and the female reproductive part of the flower. |
| It is the male reproductive part of a flower | It is the female reproductive part of the flower. |
| Androecium is composed of one or more stamens | Gynoecium is made up of one or more carpels |
| Each stamen consists of filament , an ther and a connective. | A carpel consists of three parts namely stigma, style and ovary. |
| Androecium produces the male gametes | Gynoecium produces the female gametes. |
(d) Difference between Hypogyny and Perigyny
| Hypogyny | Perigyny |
| In this flower, the ovary occupies the highest position on the thalamus. | In this condition, the margin of the thalamus grows upwards to form a cup shaped structure called calyx tube enclosing the ovary. |
| Here, the petals, sepals and stamens are separately inserted below the ovary. | Here, other parts of the flower are located on the rim of the thalamus almost at the same level as the ovary. |
| The ovary in such flowers is said to be superior. | The ovary here is said to be half inferior. |
| Examples: Mustard and china rose | Examples: Plum and rose |
(e) Difference between A complete flower and an Incomplete Flower
| Complete flower | Incomplete flower |
| A flower having all four whorls is said to be a complete flower | A flower lacking one whorl out of the four whorls is said to be an incomplete flower. |
| Example: Cotton | Example: Cucurbits |
6. What do you mean by persistent calyx?
Answer
Answer
In certain flowers like tomato and brinjal, the calyx remains attached even after the formation of the fruit and does not wither away. Such calyx is called persistent calyx.
7. Explain the function of Calyx.
Answer
Calyx is the outermost whorl of a flower which is composed of sepals. Generally these sepals are green, leaf like and protect the inner whorls of the flower in bud condition. They are also involved in producing food by photosynthesis.
8. How many whorls are present in a typical flower? Write the names of the components of every whorl.
Answer
There are 4 whorls present in a typical flower.
| Whorls | Components |
| Calyx | Sepals |
| Corolla | Petals |
| Androecium | Stamen (anther, filament and connective) |
| Gynoecium | Carpels (stigma, style and ovary) |
9. What is corolla? Write the name of its unit.
Answer
Answer
Corolla is the second whorl composed of floral leaves called petals. Petals are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination. Petals also protect the inner whorls. The shape and colour of corolla vary greatly in plants.
10. What do you mean by essential and non-essential parts of flowers? Give their functions.
Answer
Answer
The androecium and gynoecium are the essential parts of a flower because they are involved in sexual reproduction.
Androecium is the male reproductive organ of a flower and is involved in producing male gametes.
Gynoecium is the female reproductive part of the flower and produces the female gametes.
The non-essential or accessory parts of flowers are the calyx and corolla since they do not directly participate in the process of sexual reproduction leading to the development of seed.
Sepals of calyx are green, leaf like and protect the inner whorls of the flower in bud stage.
They are also involved in producing food by photosynthesis.
Petals of corolla are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination; they also protect the inner whorls.
Androecium is the male reproductive organ of a flower and is involved in producing male gametes.
Gynoecium is the female reproductive part of the flower and produces the female gametes.
The non-essential or accessory parts of flowers are the calyx and corolla since they do not directly participate in the process of sexual reproduction leading to the development of seed.
Sepals of calyx are green, leaf like and protect the inner whorls of the flower in bud stage.
They are also involved in producing food by photosynthesis.
Petals of corolla are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination; they also protect the inner whorls.
11. What do you mean by hypogynous, perigynous and epigynous ovary?
Answer
- In hypogynous flower, the ovary occupies the highest position on the thalamus, while the petals, sepals and stamens are separately inserted below the ovary. the ovary in such flowers is said to be superior. E.g., Mustard and china rose.
- In perigynous flower, the margin of the thalamus grows upwards to from a cup-shaped structure called calyx tube enclosing the ovary. the ovary here is said to be half inferior. E.g., plum and rose
- In epigynous flower, the margin of thalamus grows upwards enclosing the ovary completely and getting fused with it. the other part of the flower are above the ovary. Hence, the ovary is said to be inferior. E.g. Sunflower, flowers of cucumber.
12. Differentiate between:
(a) Flower and Inflorescence(b) Racemose and Cymose inflorescence
(c) Marginal and Parietal placentation
(d) Ray florets and Disc florets
Answer
(a) Difference between Inflorescence and Flower
| Inflorenscence | Flower |
| It refers to the arrangement of flowerson the floral axis. | Flower is modified shoot in which internodes are shortened and leaves modified into floral structure. |
| Inflorescence is of two types - Racemose and cymose. | Flower are six types - complete, incomplete, bisexual, unisexual, antinomorphic and zygomorphic. |
(b) Difference between Racemose and Cymose inflorescence
| Racemose inflorescence | Cymose inflorescence |
| Here oldest flower is at the base while the youngest flower is at the apex. | Here oldest flower is in the centre and youngest flower towards the periphery. |
| Here the main axis continues to grow. | Here, the main axis terminates in a flower, hence it is limited in growth. |
(c) Difference between Marginal and Parietal placentation
| Marginal placentation | Parietal placentation |
| There is a single placenta | Two or more placenta are present |
| The single placenta develops along the junction of the two fused margins. | The ovary is unilocular and has two or more longitudinal placenta. |
| Example: Pea | Example: Argemone |
(d) Difference between Ray florets and Disc florets
| Ray florets | Disc florets |
| They are arranged on the rim of the receptacle | They are grouped in the centre. |
| These florents may be sterile or fertile. | These florets are bisexual. |
| They are zygomorphic. | They are actinomorphic. |
13. Write four lines on the following:
(a) Androecium
(b) Gynoecium
(c) Calyx
(d) Corolla
(a) Androecium
(b) Gynoecium
(c) Calyx
(d) Corolla
Answer
(a) Androecium – It is the third whorl and is the male reproductive organ of a flower. Androecium is composed of one or more stamens. Each stamen consists of three parts:
Filament, Anther and Connective. The pollen grains are produced in pollen-sacs on the anthers.
(b) Gynoecium – It is the innermost whorl and is the female reproductive part of the flower. Gynoecium is made up of one or more carpels. A carpel consists of three parts namely stigma, style and ovary. Ovary is the swollen basal part containing ovules.
(c) Calyx – The calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower and its members are called sepals. Generally, sepals are green, leaf like and protect the inner whorls of the flower in bud stage. They are also involved in producing food by photosynthesis. The calyx may be gamosepalous (sepals united) or polysepalous (sepals free).
(d) Corolla – It is the second whorl composed of floral leaves called petals. Petals are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination. Petals also protect the inner whorls. Like calyx, corolla may be also free (gamopetalous) or united (polypetalous).
Filament, Anther and Connective. The pollen grains are produced in pollen-sacs on the anthers.
(b) Gynoecium – It is the innermost whorl and is the female reproductive part of the flower. Gynoecium is made up of one or more carpels. A carpel consists of three parts namely stigma, style and ovary. Ovary is the swollen basal part containing ovules.
(c) Calyx – The calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower and its members are called sepals. Generally, sepals are green, leaf like and protect the inner whorls of the flower in bud stage. They are also involved in producing food by photosynthesis. The calyx may be gamosepalous (sepals united) or polysepalous (sepals free).
(d) Corolla – It is the second whorl composed of floral leaves called petals. Petals are usually brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination. Petals also protect the inner whorls. Like calyx, corolla may be also free (gamopetalous) or united (polypetalous).
14. Give one example of each of the following:
(a) Actinomorphic flower
(b) Complete flower
(c) Bisexual flower
(d) Inferior ovary
(e) Persistent calyx
(f) Catkin inflorescence
Answer
(a) Actinomorphic flower
(b) Complete flower
(c) Bisexual flower
(d) Inferior ovary
(e) Persistent calyx
(f) Catkin inflorescence
Answer
(a) Datura
(b) Cotton
(c) Cotton
(d) Sunflower
(e) Tomato
(f) Mulberry
(b) Cotton
(c) Cotton
(d) Sunflower
(e) Tomato
(f) Mulberry
15. Every question has four options. Choose the correct answer.
(i) Thalamus is a
(a) stem
(b) condensed stem
(c) plumule
(d) condensed plumule
(a) stem
(b) condensed stem
(c) plumule
(d) condensed plumule
Answer
(b) condensed stem
(ii) Meaning of gamosepalous is
(a) free calyx
(b) jointed calyx
(c) calyx petaloid
(d) spiny calyx
(a) free calyx
(b) jointed calyx
(c) calyx petaloid
(d) spiny calyx
Answer
(b) jointed calyx
(iii) Four whorls of a flower are located on
(a) flower axis
(b) pedicel
(c) thalamus
(d) none of these
(b) pedicel
(c) thalamus
(d) none of these
Answer
(c) thalamus
(c) thalamus
(iv) The shape of anther in shoe-flower is
(a) reniform
(b) rounded
(c) linear
(d) appendiculate
(a) reniform
(b) rounded
(c) linear
(d) appendiculate
Answer
(a) reniform
(a) reniform
(v) Sunflower's inflorescence is
(a) corymb
(b) umbel
(c) capitulum
(d) cyathium
(a) corymb
(b) umbel
(c) capitulum
(d) cyathium
Answer
(c) capitulum