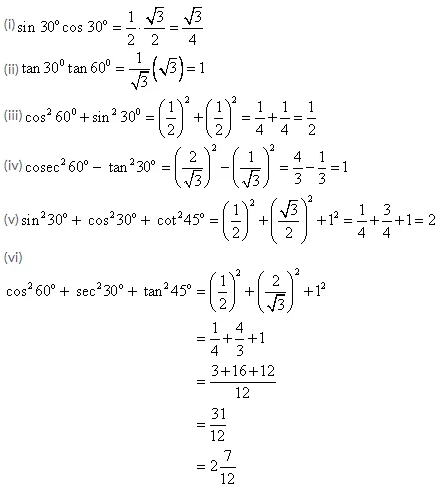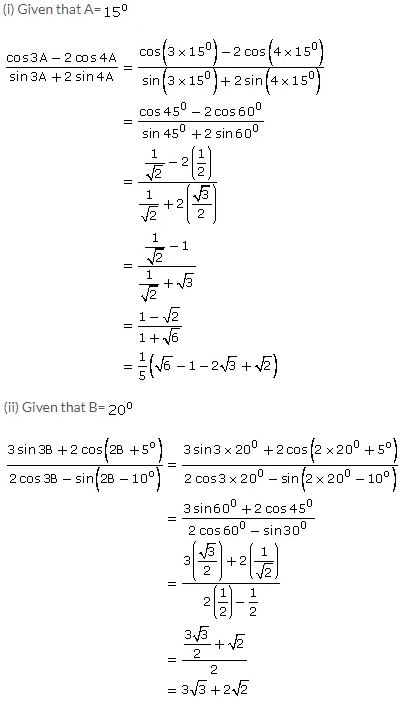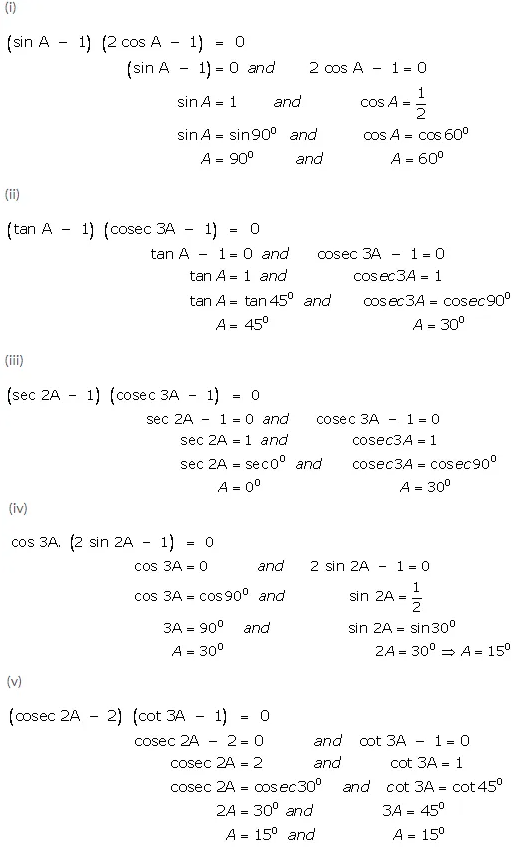ICSE Solutions for Selina Concise Chapter 23 Trigonometrical Ratios of Standard Angles Class 9 Maths
Exercise 23(A)
1. find the value of:
(i) sin 30o cos 30o
(ii) tan 30o tan 60o
(iii) cos260o + sin230o
(iv) cosec260o – tan230o
(v) sin230o + cos230o + cot245o
(vi) cos260o + sec230o + tan245o.
Answer2. find the value of :
(i) tan2 30o + tan2 45o + tan2 60o
(ii) tan45°/cosec30° + sec60°/cot45° - 5sin90°/2cos0°
(iii) 3 sin2 30o + 2 tan2 60o – 5 cos2 45o.
Answer
3. Prove that:
(i) sin 60o cos 30o + cos 60o. sin 30o = 1
(ii) cos 30o. cos 60o – sin 30o. sin 60o = 0
(iii) cosec2 45o – cot2 45o = 1
(iv) cos2 30o – sin2 30o = cos 60o.
(v) [(tan60° + 1)/(tan60° + 1)]2 = (1+cos30°)/(1-cos30°)
(vi) 3 cosec2 60o – 2 cot2 30o + sec2 45o = 0.
4. Without using table prove that:
(i) sin (2 × 30o) = 2tan30°/(1+tan2 30°)
(ii) cos (2 × 30o) = (1-tan2 30°)/(1+tan2 30°)
(iii) tan (2 ×30o) = 2tan30°/(1 - tan2 30°)
5. ABC is an isosceles right-angled triangle. Assuming of AB = BC = x, find the value of each of the following trigonometric ratios:
(i) sin 45o
(ii) cos 45o
(iii) tan 45o
6. Prove that:
(i) sin 60o = 2 sin 30o cos 30o.
(ii) 4 (sin4 30o + cos4 60o) -3 (cos2 45o – sin2 90o) = 2
Answer7. (i) If sin x = cos x and x is acute, state the value of x.
(ii) If sec A = cosec A and 0o ≤ A ≤ 90o, state the value of A.
(iii) If tan θ = cot θ and 0o ≤ θ ≤ 90o, state the value of θ.
(iv) If sin x = cos y; write the relation between x and y, if both the angles x and y are acute.
8. (i) If sin x = cos y, then x + y = 45o ; write true of false.
(ii) secθ. cotθ = cosecθ; write true or false.
(iii) For any angle, state the value of : sin2θ+ cos2θ
Answer9. State for any acute angle whether:
(i) sin θ increases or decreases as θ increases:
(ii) cos θ increases or decreases as θ increases.
(iii) tan θ increases or decreases as θ decreases.
(i) For acute angles, remember what sine means: opposite over hypotenuse. If we increase the angle, then the opposite side gets larger. That means “opposite/hypotenuse” gets larger or increases.
(ii) For acute angles, remember what cosine means: base over hypotenuse. If we increase the angle, then the hypotenuse side gets larger. That means “base/hypotenuse” gets smaller or decreases.
(iii) For acute angles, remember what tangent means: opposite over base. If we decrease the angle, then the opposite side gets smaller. That means “opposite/base” gets decreases.
10. If √3 = 1.732, find (correct to two decimal place) the value of each of the following:
(i) sin 60o
(ii) 2/tan 30°
Answer11. Evaluate:
(i) (cos 3A - 2cos 4A)/(sin 3A + 2sin 4A), when A = 15o.
(ii) [3 sin 3B + 2cos(2b + 5°)]/[2 cos3B - sin(2B - 10°); when B = 20o.
AnswerExercise 23(B)
1. Given A = 60o and B = 30o, prove that:
(i) sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B
(ii) cos (A + B) = cos A cos B – sin A sin B
(iii) cos (A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
(iv) tan (A – B) = (tan A - tan B)/(1+tan A.tan B)
Answer2. If A =30o, then prove that:
(i) sin 2A = 2sin A cos A = 2tanA/(1+tan2A)
(ii) cos 2A = cos2A – sin2A = (1-tan2A)/(1+tan2A)
(iii) 2 cos2 A – 1 = 1 – 2 sin2A
(iv) sin 3A = 3 sin A – 4 sin3A.
Answer3. If A = B = 45o, show that:
(i) sin (A – B) = sin A cos B – cos A sin B
(ii) cos (A + B) = cos A cos B – sin A sin B
4. If A = 30o; show that:
(i) sin 3 A = 4 sin A sin (60o – A) sin (60o + A)
(ii) (sin A – cos A)2 = 1 – sin 2A
(iii) cos 2A = cos4 A – sin4 A
(iv) (1- cos2A)/sin2A = tan A
(v) (1+sin2A + cos2A)/(sin A+ cos A) = 2 cos A.
(vi) 4 cos A cos (60o – A). cos (60o + A) = cos 3A
(vii) (cos3 A - cos 3A)/cosA + (sin3 A - sin3A)/sinA = 3
AnswerExercise 23(C)
1. Solve the following equations for A, if :
(i) 2 sin A = 1
(ii) 2 cos 2 A = 1
(iii) sin 3 A = √3/2
(iv) sec 2 A = 2
(v) √3 tan A = 1
(vi) tan 3 A = 1
(vii) 2 sin 3 A = 1
(viii) √3 cot 2 A = 1
Answer
2. Calculate the value of A, if :
(i) (sin A – 1) (2 cos A – 1) = 0
(ii) (tan A – 1) (cosec 3A – 1) = 0
(iii) (sec 2A – 1) (cosec 3A – 1) = 0
(iv) cos 3A. (2 sin 2A – 1) = 0
(v) (cosec 2A – 2) (cot 3A – 1) = 0
Answer3. If 2 sin xo – 1 = 0 and xo is an acute angle; find :
(i) sin xo
(ii) xo
(iii) cos xo and tan xo.
4. If 4 cos2xo – 1 = 0 and 0 ≤ xo ≤ 90o, find:
(i) xo
(ii) sin2 xo + cos2 xo
(iii) 1/cos2 x° - tan2 x°
Answer5. If 4 sin2θ- 1= 0 and angle is less than 90o, find the value of and hence the value of cos2θ + tan2θ.
Answer6. If sin 3A = 1 and 0 A 90o, find:
(i) sin A
(ii) cos 2A
(iii) tan2A – 1/cos² A
Answersin 3A = 1
⇒sin 3A = sin90°
⇒ 3A = 90°
⇒ A = 30°
7. If 2 cos 2A = √3 and A is acute, find:
(i) A
(ii) sin 3A
(iii) sin2 (75o – A) + cos2 (45o +A)
Answer8. (i) If sin x + cos y = 1 and x = 30o, find the value of y.
(ii) If 3 tan A – 5 cos B = √3 and B = 90o, find the value of A.
Answer9. From the given figure, find:
(i) cos xo
(ii) xo
(iii) 1/tan2x° - 1/sin2x°
(iv) Use tan xo, to find the value of y.
Answer10. Use the given figure to find:
(i) tan θo
(ii) θo
(iii) sin2θo – cos2θo
(iv) Use sinθo to find the value of x.
Answer11. Find the magnitude of angle A, if:
(i) 2 sin A cos A – cos A – 2 sin A + 1 = 0
(ii) tan A – 2 cos A tan A + 2 cos A – 1 = 0
(iii) 2 cos2 A – 3 cos A + 1 = 0
(iv) 2 tan 3A cos 3A – tan 3A + 1 = 2 cos 3A
Answer12. Solve for x:
(i) 2 cos 3x – 1 = 0
(ii) cos = 0
(iii) sin (x + 10o) = 1/2
(iv) cos (2x – 30o) = 0
(v) 2 cos (3x – 15o) = 1
(vi) tan2 (x – 5o) = 3
(vii) 3 tan2 (2x – 20o) = 1
(viii) cos [(x/2) + 10] =√3/2
(ix) sin2 x + sin2 30o = 1
(x) cos2 30o + cos2 x = 1
(xi) cos2 30o + sin2 2x = 1
(xii) sin2 60o + cos2 (3x- 9o) = 1
Answer13. If 4 cos2 x = 3 and x is an acute angle; find the value of :
(i) x
(ii) cos2 x + cot2 x
(iii) cos 3x
(iv) sin 2x
Answer14. In ABC, B = 90o, AB = y units, BC = units, AC = 2 units and angle A = xo, find:
(i) sin xo
(ii) xo
(iii) tan xo
(iv) use cos xo to find the value of y.
Answer15. If 2 cos (A + B) = 2 sin (A – B) = 1; find the values of A and B.
Answer 15: